Describe Brachial Artery Under The Following Heads
Table of Contents
1. Brachial Artery Origin,
2. Brachial Artery Course and Relations,
3. Brachial Artery Branches, and
4. Brachial Artery Applied anatomy
Answer:
1. Brachial Artery Origin
It is the continuation of the axillary artery distal to the lower border of teres major
2. Brachial Artery Course and relations
Peculiarities:
It is superficial throughout its course. It is accompanied by
1. Veins: Venae commitments (brachial veins)
Read And Learn More: Anatomy Notes And Important Questions and Answers
Nerves accompanying the brachial artery and its branches
- The brachial artery accompanies the median nerve in the upper half of the arm.
- The superior ulnar collateral artery, a branch of the brachial artery, accompanies the median nerve in the lower half of the arm,
- Profunda brachii (a branch of the brachial artery) accompanies the radial nerve,
- Anterior descending artery (a branch of the profunda brachial artery) accompanies the radial nerve, and
- The superior ulnar collateral artery (a branch of the brachial artery) accompanies the ulnar nerve.
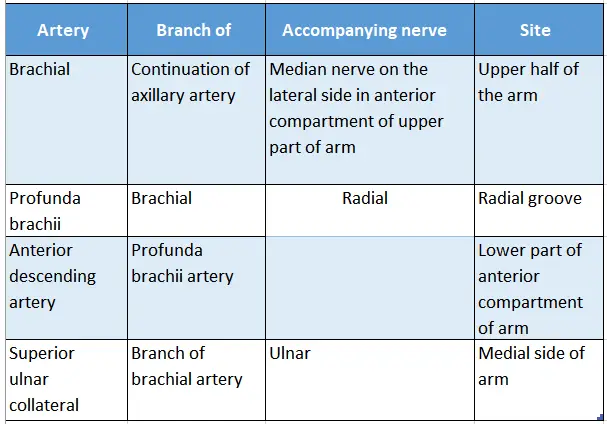
Brachial Artery Relations
1. Anterior
- Skin,
- Superficial fascia,
- Deep fascia,
- Biceps brachii, and
- Bicipital aponeurosis at the bifurcation.
2. Posterior
- The long head of triceps,
- Medial head of
- Coracobrachialis, and
- Brachialis.
3. Lateral: Upper part median nerve.
4. Medial
- The medial cutaneous nerve of the arm, and
- The lower part of the median nerve.
Termination: The artery divides at the neck of the radius into radial and ulnar arteries.
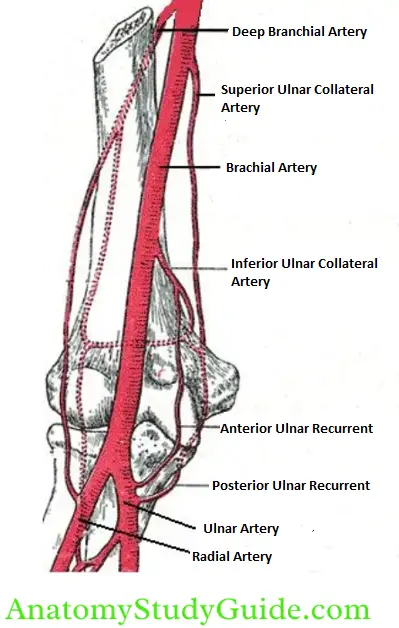
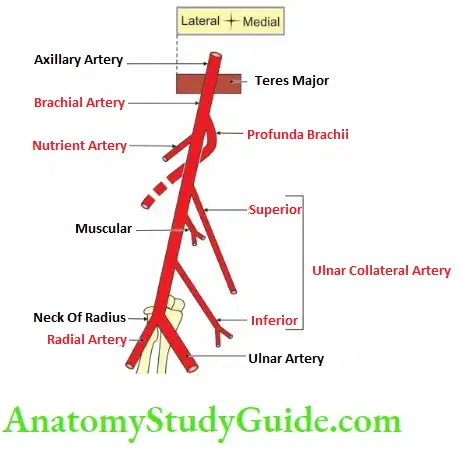
3. Brachial Artery Branches
1. Cutaneous to the skin over the arm,
2. Muscular: Muscles of the arm (deltoid, biceps, brachialis, coracobrachialis),
3. Articular branches to
1. Shoulder joint,
2. Elbow joint by
- Superior ulnar collateral, and
- Inferior ulnar collateral artery
4. Nutrient branch to the humerus,
5. Anastomotic branch to the posterior circumflex humeral artery, and
6. Terminal branches: Radial and ulnar arteries.
4. Brachial Artery Applied Anatomy
- The brachial artery is ruptured in a supracondylar fracture of the humerus leading to Volkmann’s ischaemic contracture.
- The pulsations of the brachial artery are felt or auscultated in front of the elbow medial to the tendon of the biceps.
- Haemorrhage due to the brachial artery can be controlled by direct compression of the brachial artery. The compression should be in the middle of the arm on the tendon of the coracobrachialis and medial to the humerus.
- Blood pressure is recorded by auscultation of the pulsations of the brachial artery in the cubital fossa.
- The blood for blood gas analysis is collected from the brachial artery.
- The pulsations of the brachial artery are felt or auscultated in front of the elbow medial to the tendon of the biceps.
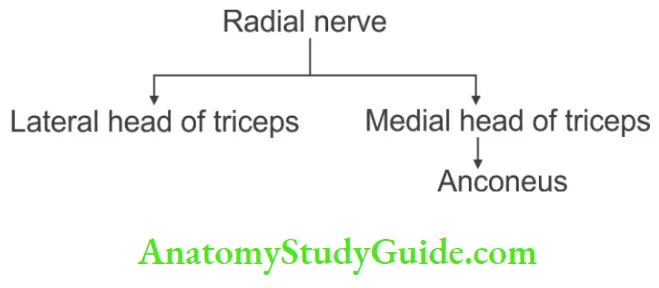
Branches Of Radial Nerve In Radial Groove
- Branch to the medial head of triceps,
- Branch to the lateral head of the triceps, and
- Anconeus.
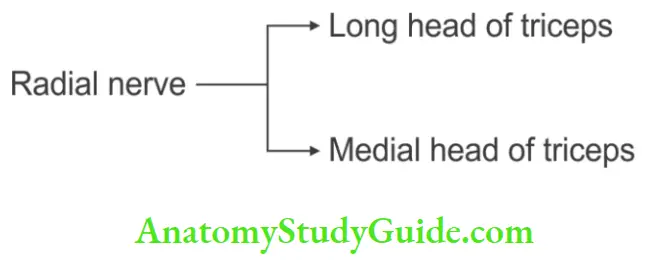
Branches Of Radial Nerve In Axilla
- The long head of triceps, and
- The medial head of the triceps.
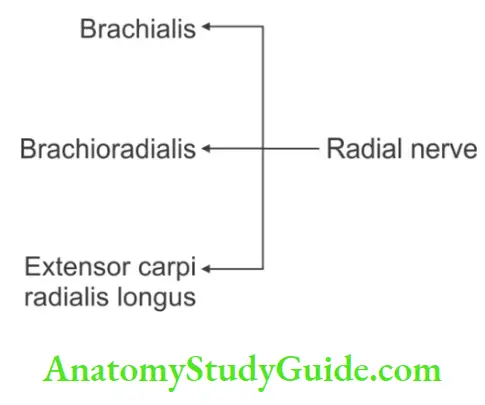
Branches Of Radial Nerve In Front Of Lower Part Of Arm
1. Muscular branch
- Brachioradialis,
- Extensor carpi radialis longus, and
2. Proprioceptive branch to brachialis.
Leave a Reply