Carving Of The Permanent Canines
The steps in carving of the permanent maxillary canine will be described in detail. The permanent mandibular canine can be carved following the same steps but with variation in features.
Table of Contents
Carving Of The Permanent Maxillary Right Canine
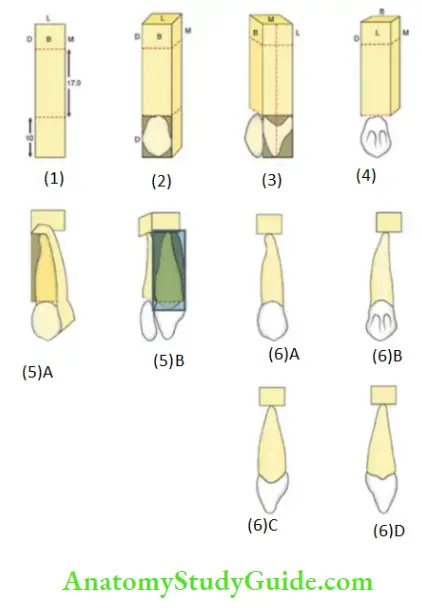
1. Mark the cervico-incisal dimension of the crown and the root on the wax block. The portion of the wax block beyond the root is called the base. Label the surfaces at the bottom of the block as B, L, M, D indicating Buccal, Lingual, Mesial and Distal.
Note: B is used instead of L (for labial) to avoid confusion.
Read And Learn More: Oral Physiology Notes
2. Mark the mesio-distal dimension on the buccal surface of the crown at the cervical line and at the contact area. Draw the outline of the labial aspect on the crown with the distal slope longer than the mesial slope. Carve the wax outside the outline (shaded portion) and thus create the mesial and distal surface of the crown. Mark the midline of the block on the proximal aspect.
3. Mark the midline on the proximal aspect. Mark the labio-lingual dimension of the crown at the cervical line, at the crest of curvature and the cusp tip. The cusp tip has to pass through the midline of the block. Carve the wax outside the outline (shaded portion) and thus create the labial and the lingual outline of the crown with the lingual surface being narrower( lingual narrower) than the labial surface. Carve the labial ridge on the labial surface.
4. Carve the mesial and the distal lingual fossa with the lingual ridge in between the two fossa. The lingual fossa can be carefully carved with the discoid portion of the instrument.
5. Mark the shape of the root on the buccal and proximal side of the wax block and carve the wax outside the outline of the root (shaded portion).
Make the root lingually converging.
6. Check for the dimension and complete carving the anatomy of the tooth in detail. Carve the cervical line and polish the tooth. The steps in carving the permanent mandibular canine are the same.
The exceptions are mentioned below:
- Dimensions of the crown and the root.
- Outlines.
- The cusp tip is lingual to the midline.
- The cingulum is distally placed.
- The crown appears to be twisted on the root base.
- The mesial outline of the crown is in line with the mesial outline of the root.
Leave a Reply