Question 1. Organism causing acute bacterial prostatitis
- Streptococcus viridans
- Peptostreptococcus
- coli
- Enterococcus
Answer. (3) (coli)
Most common cause of Bacterial prostatitis Escherichia coli.
Read And Learn More: Micro Biology And Immunology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 2. Which is not an important cause of neonatal sepsis?
- coli
- Group B Streptococci
- Acinetobacter
- Staph. auerus
Answer. (3) (Acinetobacter)
Among the options, Acinetobacter is the best answer.
The infectious agents associated with sepsis in pediatric patients:
- In the neonatal age group, group B streptococcus, Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, enteroviruses, and herpes simplex virus are the pathogens most commonly associated with sepsis.
- In older children Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Staphylococcus aureus are more common.
- Toxic shock syndrome from group A streptococcus or S. aureus can also be seen in older children.
- Infections with gram-negative bacteria (e.g. Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas,
Acinetobacter, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia) and fungi (e.g. Candida,Aspergillus) most often occur in immunocompromised and hospitalized patients colonized with these organisms. - Pseudobacteremia may be associated with contaminated heparin flush solutions,intravenous solutions, albumin, cryoprecipitate, and infusion equipment. Contaminants include waterborne organisms, such as Burkholderia cepacia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Serratia.
Question 3. Enterobacteriaceae are:
- Pseudomonas
- Klebsiella
- V. cholerae
- Proteus
- E.coli
Answer. (2, 4, 5) (Klebsiella, Proteus, E.coli)
Question 4. A chronic alcoholic patient is presented with necrotic pneumoniSputum culture reveals mucoid lactose fermenting colonies on MacConkey medium. What is the organism?
- Klebsiella
- coli
- Moraxella catarralis
- Burkholderia
Answer. (1) (Klebsiella)
- Mucoid lactose fermenting colonies on MacConkey medium- Suggestive of Klebsiella.
Question 5. Which is not member of enterobacteriaceae family?
- E.coli
- Salmonella
- Citrobacter
- Vibrio
- Pseudomonas
DIARRHEAGENIC COLI
Answer. (4, 5) (Vibrio, Pseudomonas)
- Vibrio and Pseudomonas are not members of enterobacteriaceae family
Question 6. Identify the organism which ·shows effacement and attachment of intestinal cells as shown below?

- EPEC
- ETEC
- Enterohemorrhagic coli
- Diffusely enteroadherent coli
Answer. (1) (EPEC)
- Effacement and attachment of intestinal mucosa is usually a feature of
Enteropathogenic coli - A/E lesions (attaching and effacing lesions): EPEC induces typical lesions on the intestinal epithelium (coded by chromosomal LEE gene, i.locus for enterocyte effacement); which leads to disruption of brush border epithelium causing increased secretion and watery diarrhea
Question 7. EHEC strain associated with HUS is:
- O157 : H7
- O7 : H157
- O37 : H14
- O157 : H9
Answer. (1) (O157: H7)
- HUS is caused by EHEC strain O157:H7.
Question 8. MC cause of diarrhea in children of developing country is:
- EHEC
- ETEC
- EPEC
- EIEC
Answer. (3) (EPEC)
- Next to Rotavirus, EPEC is the MC cause of diarrhea in children of developing country.
Question 9. Traveller’s diarrhea is caused by:
- ETEC
- EHEC
- EPEC
- EIEC
Answer. (1) (ETEC)
- ETEC is the MC cause of traveler’s diarrhea.
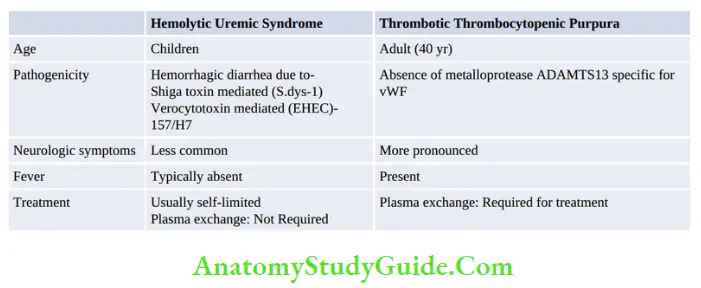
Question 10. Which of the following is not true about HUS?
- May present with hemorrhagic colitis
- Shiga like toxin has no role in HUS
- Usually self-limited
- Fever is typically absent
Answer. (2) (Shiga-like toxin has no role in HUS)
Question 11. Culture media used for diagnosis of EHEC O157: H7 is:
- O7 culture
- Sorbitol MacConkey media
- XLD agar
- Deoxycholate media
Answer. (2) (Sorbitol MacConkey media)
- EHEC can be differentiated from other coli as it is sorbitol non fermenter, hence it produces colorless colony on Sorbitol MacConkey media whereas others can ferment sorbitol producing pink colony.
Question 12. A 20-year-old man presented with hemorrhagic colitis. The stool sample grew Escherichia coli in pure culture
The following serotype of coli is likely to be causative agent:
- O157:H7
- O159:H9
- O107:H7
- O55:H7
Answer. (1) (O157:H7)
- Enterohemorrhagic coli dysentery can lead to complications like hemorrhagic uremic syndrome and hemorrhagic colitis.
- Serotypes’ associated with EHEC are O157:H7 and O26:H1
- Similar illnesses also produced by Shigella dysenteriae type1.
Question 13. MC cause of HUS in developing country:
- EHEC
- Shigella dysentriae type 1
- ETEC
- Pneumococcus
Answer. (2) (S. dysentriae type 1)
MC cause of HUS in developing country is Shigella dysentriae type 1; whereas in developed country, it is EHEC O157:H7.
Question 14. Sereny test is employed for laboratory diagnosis of:
- a.Enterotoxigenic coli
- Enteropathogenic coil
- Enterohaemorrhagic coil
- Enteroinvasive coli
Answer. (4) (Enteroinvasive coli)
Sereny’s test is an animal pathogenicity test employed for laboratory diagnosis of Enteroinvasive coli and Shigella.Instillation of organism into the eyes of guinea pigs leads to conjunctivitis and severe keratitis.
Question 15. Most common cause of pyelonephritis in pregnant women:
- E.coli
- Klebsiella
- N. gonorrhea
- S. aureus
Answer. (1) (coli)
E.coli is the most common cause of UTI-Both upper UTI (pyelonephritis) and Lower UTI (Cystitis).
Question 16. Regular drinking of which of the following can help prevent UTI?
- Grape juice
- Raspberry juice
- Orange juice
- Cranberry juice
Answer. (4) (Cranberry juice)
An ex-vivo study’. Int. journal of immunopathology and pharmacology, Tempera et al 2010-23 (2): 611–8.
- Cranberry juice may help prevent and relieve the symptoms of urinary tract infections
- Mainly by 3 mechanisms:
- Directly by altering the molecular structure of the fimbriae on the pathogenic strains.
- Proanthocyanidins in cranberries prevents the bacteria adherence to the bladder and urinary tract.
- Indirectly on the bacteria by reducing the intravesical pH.
Question 17. A young lady presents with fever, dysuria and pain abdomen. Uncomplicated acute cystitis was diagnoseWhich among the following is not true?
- E.coli count of <103/mL
- 1 pus cell per 7 fields
- 1 bacilli per field
- Nitrate test positive
Answer. (1) (coli count of < 103/mL)
- UTI is diagnosed when the bacterial count exceeds 105/ml of urine (significant Bacteriuria).
- About other options
- Option (2): ‘Under appropriate condition, finding of 1 leukocyte per 7 high power field correlates with 104 leucocytes/ml and which implies significant’.
- Option (3): Gram staining is not a reliable method to estimate the significance of UTI.
Using >1/Oil immersion field, the sensitivity is 91% which correlates with significant Bacteriuria. - Option (4): The most common organisms causing UTI are coli (70%), Klebsiella, Proteus.
All these belong to family Enterobacteriaceae and all can reduce nitrate to nitrite.
Question 18. Which of the gram negative bacteria release histamine when it inhabits fish? It is implicated in them causing scombroid (fish) poisoning?
- Staphylococcus
- Shigella
- Salmonella
- Proteeae
Answer. (4) (Proteeae)
Scombroid poisoning
Food allergic reactions typically affect one person who has a history of allergy to the implicated food item. However, with scombroid poisoning, more than one person, often with no history of allergies, may be affected.
- Histamine produced by the decarboxylation of histidine in the muscle of the fish is primarily responsible for the condition.
- The decarboxylation process is induced by enzymes produced by primarily enteric gramnegative bacteria (e.g., Morganella morganii (most common), Escherichia coli,
Klebsiella species and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) found in the fish’s cutis and intestines. - Proteeae tribe includes Proteus, Morganella and Providencia.
Question 19. A patient with benign hypertrophy of prostate was admitted in the hospital for 3 weeks. He subsequently developed suspected catheter associated-urinary tract infection. The tip of the catheter was sent for culture and was grown on blood agar. After 24 hours, the blood agar shows the following appearancWhat is the likely causative agent for the UTI?

- Proteus mirabilis
- Pseudomonas
- Escherichia coli
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
Answer. (1) (Proteus mirabilis)
Blood agar with swarming motility is suggestive of Proteus.
Question 20. Dienes’ phenomena is seen with:
- Proteus mirabilis
- Klebsiella
- Proteus vulgaris
- Providentia
- Morganella
Answer. (1, 3) (P. mirabilis, P. vulgaris)
Diene’s phenomenon to know the relatedness between different strains of Proteus
- When two Proteus strains are streaked at two ends of a blood agar, they start swarming and join to each other.
- If both the strains are related, there will not be any line of separation and if both the strains are not related, they will be separated by a line of demarcation.
Question 21. All of the following are true except:
- coli is an aerobe and facultative anaerobe
- Proteus forms uric acid stones
- coli is motile by peritrichous flagella
- Proteus causes deamination of phenylalanine to phenylpyruvic acid
- Klebsiella
Answer. (2) (Proteus forms uric acid stones)
Proteus forms struvite stone in bladder in alkaline urine.
Question 22. The colonies grown in MacConkey agar belongs to:
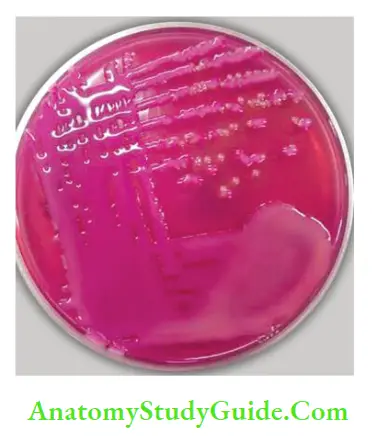
- E.coli
- Pseudomonas
- Klebsiella
- SHIGELLA
Answer. (3) (Klebsiella)
Question 23. Late lactose fermenting Shigella:
- S. sonnei
- S. flexneri
- S. boydii
- S. dysenteriae
Answer. (1) (S. sonnei)
Question 24. All are catalase positive except:
- Shigella flexneri
- Shigella boydii
- Shigella dysenteriae type 1
- Shigella sonnei
Answer. (3) (S. dysenteriae type 1)
Question 25. In Tropical countries (India) bacillary dysentery is by:
- Shigella dysentriae
- Shigella flexneri
- Shigella sonnei
- Shigella boydii
Answer. (2) (S. flexneri)
Bacillary dysentery is caused by Shigella species:
- In India and other tropical countries- MC Shigella species is S. flexneri
- In developed countries- MC Shigella species is S. sonnei.
Question 26. Which of the following drugs is not used in typhoid fever?
- Amikacin
- Cefixime
- Ciprofloxacin
- Azithromycin
Answer. (1) (Amikacin)
- Drugs used for typhoid fever are cefixime, ciprofloxacin, azithromycin, ceftriaxone, chloramphenicol, cotrimoxazole and ampicillin.
Question 27. Salmonella-like diarrhea is associated with:
- Enteroaggregative coli. persistent diarrhea
- Enterotoxigenic coli—travellers’ diarrhea
- Enteropathogenic coli—infantile diarrhea
- EHEC—HUS
Answer. (4) (EHEC—HUS)
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) has been associated with typhoid fever (Salmonella typhi).
Question 28. A boy is presented with multiple nonsuppurative osteomyelitis with sickle cell anemia.What will be the causative agent?
- Salmonella
- S. aureus
- H. influenzae
- Enterobacter species
Answer. (1) (Salmonella)
Salmonella osteomyelitis is commonly associated with sickle cell disease
Question 29. Vi vaccine can be given at what age?
- 6 months
- 12 months
- 24 months
- 18 months
Answer. (3) (24 months)
Vi vaccine is given only after 2 years of agCapsular antigen being T independent antigen,is poorly immunogenic to children <2 years
Question 30. Salmonella typhi is the causative agent of typhoid fever. The infective dose of S. typhi is:
- One bacillus
- 108–1010 bacilli
- 102–105 bacilli
- 1–10 bacilli
Answer. (3) (102 –105 bacilli)
- All Salmonella infections begin with ingestion of organisms, most commonly in contaminated food or water. The infectious dose is 103–106 colony-forming units.
Question 31. A 15-year-old girl had splenomegaly, leucopenia, fever and died in a few days. Longitudinal ulcers were found in intestin What should be the probable diagnosis?
- Typhoid
- Tuberculosis
- Amebiasis
Answer. (1) (Typhoid)
- Splenomegaly, leucopenia, fever and Longitudinal ulcers found in intestine are characteristic features of enteric fever.
Question 32. All are correct regarding widal test, except:
- Baseline titer differs depending on the endemicity of the disease
- High titer value is a single widal test is not confirmative
- O antibody last longer and hence is not indicative of recent infection
- O antibody cannot differentiate between types
Answer. (3) (O antibody last longer and hence is not indicative of recent infection)
- O antibody appears early and goes early and rise of O Antibody without rise of H Antibody indicates recent infection.
- Details about Widal test- refer chapter review.
Question 33. All of the following salmonellae are motile except:
- S. typhi
- S. enteridis
- S. gallinarum pullorum
- S. chester
Answer. (3) (S. gallinarum pullorum)
Salmonelle are motile except S. gallinarum pullorum which are nonmotile (aphasic).
Question 34. Drug commonly used against enteric fever are all except:
- Amikacin
- Ciprofloxacin
- Ceftriaxone
- Azithromycin
Answer. (1) (Amikacin)
- Aminoglycosides are not given for enteric fever
- Treatment for Enteric fever- Refer Chapter Review.
Question 35. Incubation period of salmonella typhi:
- 2–5 days
- 3–21 days
- 14–25 days
- > 60 days
Answer. (2) (3-21 days)
- ‘The incubation period for S. Typhi averages 10–14 days but ranges from 3 to 21 days,with the duration likely reflecting the inoculum size and the host’s health and immune status.’
Question 36. Vi antigen found in:
- Salmonella paratyphi ‘A’
- Salmonella paratyphi ‘C’
- Salmonella dublin
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Citrobacter freundii
Answer. (2, 3, 5) (S. paratyphi C, S. dublin, Citrobacter)
- Vi Antigen is possessed by S typhi and S. paratyphi C, S. dublin, Citrobacter (BallerupBethesda group).
- For detailed explanation refer chapter review.
Question 37. There has been an outbreak of food born salmonella gastroenteritis in the community and the stool samples have been received in the laboratory. Which is the enrichment medium of choice?
- Cary Blair medium
- VR medium
- Selenite ‘F’ medium
- Thioglycollate medium
Answer. (3) (Selenite ‘F’ medium)
Outbreak of food born salmonella gastroenteritis
For the stool culture, 1st it has to be processed in an enrichment medium followed by streaking in a selective media.
Enrichment medium for Salmonella: Tetrathionate broth, Selenite F broth, Gram-negative broth.
Question 38. A 24-year–old cook in a hostel mess suffered from enteric fever 2 years back. The chronic carrier state in this patient can be diagnosed by: (NEET Pattern Based)
- Vi agglutination test
- Blood culture in Brain Heart infusion broth
- Widal test
- Bone marrow culture
Answer. (1) (Vi agglutiion test)
- Vi agglutinins of titer of > 1:10 is taken significant for diagnosis of Typhoidal carriers.
Question 39. In a patient with typhoid, diagnosis after 15 days of onset of fever is best done by:
- Blood culture
- Widal
- Stool culture
- Urine culture
Answer. (2) (Widal)
- ‘Agglutinins in Widal test start appearing at the end of 1st week and increases steadily till 3rd/4th week then fall.’
- Week wise diagnosis of choice of Enteric fever.
Question 40. True about typhoid:
- Female carriers- less common
- Male carriers are less common but more dangerous
- Gallbladder not involved in acrriers
- Tetracycline –DOC
Answer. (2) (Male carriers are less common but more dangerous)
- Male carriers are less common but more dangerous
- MC site of for typhoid carrier: Gallbladder and billiary tract and also urinary tract
- DOC for typhoid carrier: Ampicillin or Amoxycilin plus probenecid for 6 weeks.
Question 41. Typhoral schedule:
- 1,3,5 days
- 1,2,3,days
- 1,2,4, days
- 1,7,14 days
Answer. (1) (1,3,5 days)
- Typhoral schedule: 3 doses on alt day (1/3/5) in capsules, Effective after 7 days, Booster needed @5 years.
Question 42. H2S forming Salmonella:
- S. Typhimurium
- S. Typhi
- S. Paratyphi A
- S. Paratyphi B
- S. Cholerasuis
Answer. (1, 2, 4, 5) (S. typhimurium, S. typhi, S. paratyphi B, S. cholerasuis)
H2S forming Salmonella:
- Salmonella paratyphi -A : Absent H2S
- Salmonella paratyphi –B : Big H2S (Produce large quantity of H2S)
- Salmonella typhi and S. cholerasuis- Tiny H2S (i.small amount of H2S)
Question 43. Red pigment producing bacteria is:
- E coli
- Bordetella parapertussis
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Serratia marcescens
- Yersinia
Answer. (4) (Serratia marcescens)
Serratia marcescens produces red pigment called prodigiosin.
Question 44. True about plague:
- Seasonal spread
- No vaccine is available
- Tetracycline is used both for chemoprophylaxis and treatment
- Caused by gram-negative motile bacteria
Answer. (1, 3) (Seasonal spread, Tetracycline is used..)
- Plague outbreaks are usually seasonal in North India (from September until May) which depends on field rodent factors. No seasonality is found in South India.
- Tetracycline is DOC for chemoprophylaxis and it can also be given for treatment (DOC for treatment is Gentamicin)
- Y. pestis is gram negative but non motile.
Question 45. Children with Thalassemia and iron overload are at an increased risk for infection with:
- Yersinia enterocolitica
- Campylobacter jejuni
- Escherichia coli
- Vibrio cholerae
Answer. (1) (Yersinia enterocolitica)
Any condition involving iron overload (including thalassemia and hemochromatosis) is a risk factor for infection with Yersinia enterocolitica.
Question 46. Farmer presents with the features of high fever, painful inguinal lymphadenopathy,vomiting and diarrhea and hypotension. Which stain will help in the diagnosis?
- Neisser stain
- Wayson’s stain
- Albert’s stain
- McFadyean’s stain
Answer. (2) (Wayson’s stain)
This is a case of bubonic plague
Points in favor:
- Farmer: High risk of exposure to rodents
- Presented with high fever, painful inguinal lymphadenopathy,
- So, now we have to use a stain that will stain the causative agent Y. pestis.
- ‘When stained with a polychromatic stain (e.g. Wayson or Giemsa), Y. pestis isolated from clinical specimens exhibits a characteristic bipolar appearance, resembling closed safety pins’.
Other stains given in the question: - Neisser stain and Albert’s stain: Used to demonstrate metachromatic granules
- McFadyean’s stain: Used to demonstrate capsule of B.anthracis.
Question 47. Appendicitis-like syndrome is caused by:
- Y. pestis
- Y. pseudotuberculosis
- Pasturella septica
- Brucella abortus
Answer. (2) (Y. pseudotuberculosis)
Y. enterocolitica commonly causes terminal ileitis and Y. pseudotuberculosis commonly causes mesenteric adenitis, leading to pseudoappendicitis.
Leave a Reply