Front Lateral and Medial Sides of Leg and Dorsum of Foot
Name The Muscles Supplied By Superficial Peroneal Nerve
Table of Contents
1. Peroneus longus, and
2. Peroneus brevis.
Enumerate muscles of anterior compartment of leg
1. Tibialis anterior,
2. Extensor hallucis longus,
3. Extensor digitorum longus, and
4. Peroneus tertius.
Read And Learn More: Anatomy Notes And Important Question And Answers
Enumerate Muscles Of Lateral Compartment Of Leg
1. Peroneus longus, and
2. Peroneus brevis.
Enumerate Muscles Of Posterior Superficial Compartment Of Leg
1. Medial head of gastrocnemius,
2. Lateral head of gastrocnemius,
3. Soleus, and
4. Plantaris.
Enumerate Muscles Of Posterior Deep Compartment Of Leg
1. Popliteus,
2. Flexor digitorum longus,
3. Flexor hallucis longus, and
4. Tibialis posterior.
Name The Muscles Supplied By Deep Peroneal Nerve
1. Muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg
- Tibialis anterior,
- Extensor hallucis longus,
- Extensor digitorum longus, and
- Peroneus tertius.
2. Muscle of the dorsum of the foot: Extensor digitorum brevis
Name The Branches Of Dorsalis Pedis Artery
1. Lateral tarsal artery,
2. Medial tarsal branches,
3. Arcuate artery, and
4. Dorsal metatarsal arteries: They are 4 in number. Each artery divides into 2 dorsal digital arteries.
Peroneus Longus Muscle
Peroneus Longus Muscle Introduction: It is superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of leg.
1. Peroneus Longus Muscle Proximal attachments
- Head of the fibula,
- Upper 1/3rd, and
- Lateral surface of the shaft of the fibula (upper 2/3rd).
2. Peroneus Longus Muscle Distal attachments
- Lateral side of the base of the 1st metatarsal bone, and
- Adjoining part of the medial cuneiform bone. The tendon changes its direction below the lateral malleolus and again on the cuboid bone.
3. Peroneus Longus Muscle Peculiarities
- A sesamoid bone is present in the tendon.
- It continues as lateral collateral ligament.
4. Peroneus Longus Muscle Actions
- Evertor of foot especially when foot is off the ground.
- Maintains lateral longitudinal and transverse arch of the foot.
- Peroneus longus and tibialis anterior are inserted into the same medial cuneiform bone, the two together form a ‘stirrup’ beneath the middle of the sole.
- The presence of the sling keeps the middle of foot pulled up and prevents flattening of its arches.
- The peroneus longus and brevis come into play in extreme plantar flexion.
5. Peroneus Longus Muscle Nerve supply: Superficial peroneal nerve
6. Peroneus Longus Muscle Applied anatomy
- Paralysis of peroneus brevis and peroneus longus occurs due to injury to superficial peroneal nerve.
- The foot cannot be everted at subtalar joint.
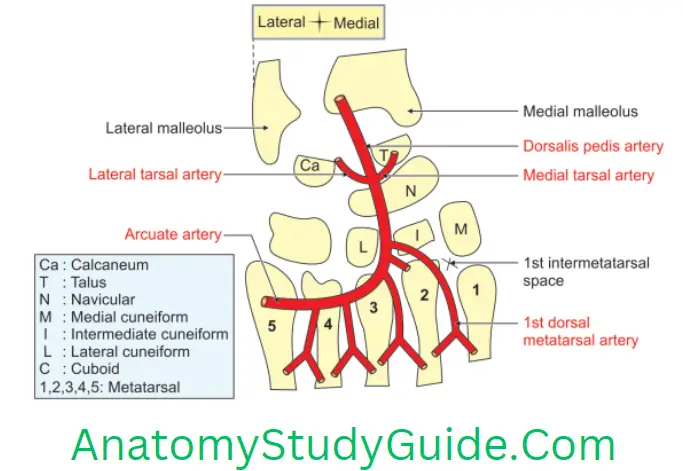
Dorsalis Pedis Artery
Dorsalis Pedis Artery Introduction: It is also called the dorsal artery of the foot. It is the chief artery of dorsum of foot.
1. Dorsalis Pedis Artery Origin: It is the continuation of anterior tibial artery in front of ankle joint, distal to inferior extensor retinaculum.
2. Dorsalis Pedis Artery Termination: It continues as deep plantar or perforating branch. In the sole, it completes the plantar arch by joining the lateral plantar artery.
3. Dorsalis Pedis Artery Extent: It extends from distal end of inferior extensor retinaculum to proximal end of 1st intermetatarsal space.
4. Dorsalis Pedis Artery Features
- This is the chief palpable artery of the dorsum of the foot.
- It behaves like the radial artery in the hand. Its main branch ends between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal bones. It reaches the plantar surface of the foot. It becomes the main contributor to the plantar (deep plantar) arch.
5. Dorsalis Pedis Artery Course
- It begins in front of the ankle joint between two malleoli (medial and lateral).
- It passes along the medial side of the dorsum of the foot.
- It reaches the proximal end of 1st intermetatarsal space. Here it pierces 1st dorsal interosseous muscle.
6. Dorsalis Pedis Artery Relations
1. Superficial: The artery is very superficial. The extensor hallucis brevis is the only structure that separates it from the skin, superficial fascia and deep fascia.
2. Deep
1. Capsular ligament of the ankle joint.
2. The tarsal bones from posterior to anterior are
- Talus,
- Navicular, and
- Intermediate cuneiform bones and the ligaments connecting them.
3. Medial: Extensor hallucis longus
4. Lateral
- 1st tendon of the extensor digitorum longus.
- Medial terminal branch of the deep peroneal nerve.
7. Dorsalis Pedis Artery Branches
- Lateral tarsal artery,
- Medial tarsal branches,
- Arcuate artery, and
- Dorsal metatarsal arteries.
8. Dorsalis Pedis Artery Applied anatomy
Dorsalis pedis artery is superficial and its pulsations are felt.
It is often palpated in patients suffering from vaso-occlusive diseases of the lower limb, viz. Buerger’s disease.
The pulsations help to
Determine the level of amputation of leg in case of gangrene of toes.
- Assess peripheral circulation.
- The artery is rarely ligated.
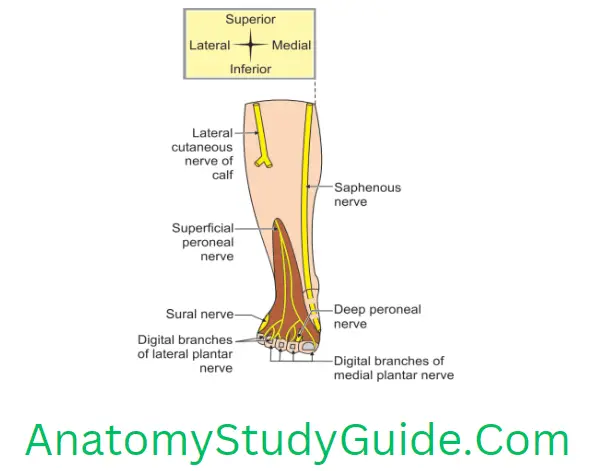
Cutaneous Nerve Supply Of Dorsum Of Foot
1. Skin of the dorsum of the foot is supplied by medial and lateral branches except
- Lateral border, supplied by sural nerve.
- Medial border up to the base of the great toe, supplied by the saphenous nerve
- Cleft between the 1st and 2nd toes, supplied by the deep peroneal nerve.
Leave a Reply