Maxillary Major Connectors Introduction
The major connector unites all other components with it and gives a unified unit that acts as a single unit as a removable partial denture. The selection of major connectors varies according to missing teeth and their location. This chapter focuses on a brief review of maxillary major connectors and their indication.
Table of Contents
Major Connector
The component of a removable partial denture connects the parts (of RPD) located on one side of the dental arch to those on the other side. Its main functions are to provide unification and rigidity to the denture.
Read and Learn More: Preclinical Prosthodontics Notes
Selection of major connector for particular edentulous maxillary arch:
- If the remaining natural teeth are periodontally weak the required support should be taken from the palate. For this, a full palatal major connector should be used.
- If the remaining natural teeth are periodontally sound and little support is required then a palatal strap or double palatal bar can be used.
- If torus is present and inoperable then use horseshoe, closed horseshoe major connector.
- Avoid the use of the palatal bar because of its greater bulk and interference with the tongue, and speech.
- For anterior teeth replacement, a horseshoe or closed horseshoe can be used.
- Major connectors in the maxillary arch should terminate 4.0 mm or more from the free gingival margin.
Maxillary Major Connectors
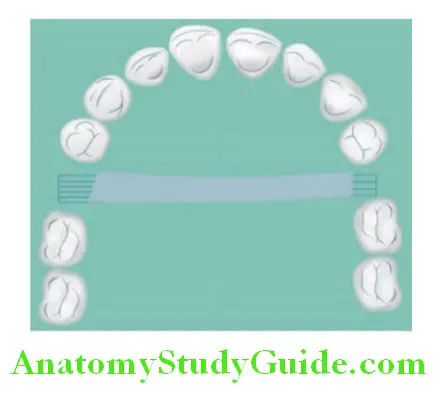
Palatal Bar (Single Posterior Palatal Bar) Major Connector:
Indications:
- Used when one or two teeth are to be replaced.
- Used with class III edentulous condition.
- Requires strong abutment.
- When present tori is noninterfering.
Advantages:
- It was widely used earlier.
- Simple design configuration.
Disadvantages:
- It is very bulky.
- Interfere with tongue movement.
- Interfere with speech.
- Cannot be used for the replacement of multiple teeth.
Palatal Strap Major Connector:
Indications:
- For a short edentulous span.
- Bilateral edentulous space.
- Tooth-supported partial denture.
Advantages:
- Less interference with tongue movements.
- More degree of resistance.
- Even distribution of load.
Disadvantages:
- More palatal coverage than palatal bar.
- More tissue reaction.
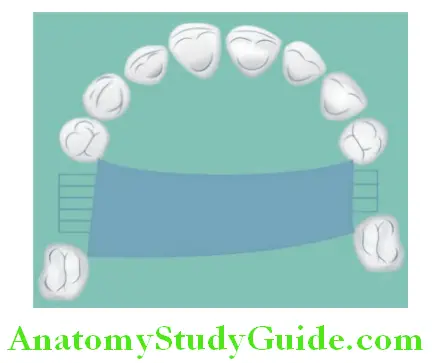
Anteroposterior (Double Palatal) Bar Major Connector:
Indications:
- Used with periodontally strong abutments.
- Used with a U-shape palate.
- Class-I partially edentulous condition.
Advantages:
- It offers excellent rigidity
- Offers less palatal coverage
- It can be used when multiple missing teeth to be replaced
Disadvantages:
- Not for high vault palate.
- Offers little support.
- The bulk of metal interferes with the tongue.
- Speech may get altered temporarily.
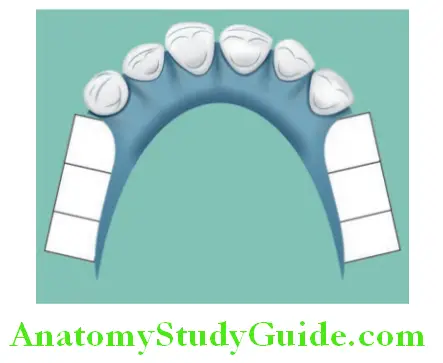
U-shaped Palatal Major Connector (Horseshoe-shaped Major Connector):
Indications:
- Indicated for class I and class IV conditions.
- When tori is present and inoperable.
- If the tori extends to the posterior part of the hard palate.
Advantages:
- Derives support and indirect retention from palatal tissue.
- When several anterior teeth are being replaced.
Disadvantages:
- When used in distal extension cases, it may flex during mastication due to posterior open ends.
- Need excess bulk in rugae.
- May interfere with speech.
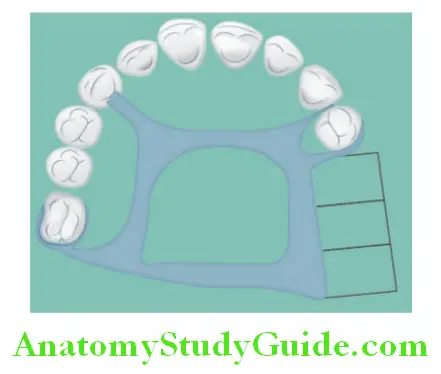
Anteroposterior Strap Major Connector:
Indications:
- Indicated for class I and class II conditions with sound abutments.
- Long edentulous span in class I with modification.
- Class-IV condition when anterior teeth are to be replaced with a removable partial denture.
- Inoperable tori but not extending to the posterior part of the palate.
Advantages:
Can be used for most of the partially edentulous conditions. Anterior and posterior straps closed by longitudinal metal extensions give a circular configuration which gives rigidity to the major connector.
Disadvantages:
- Not indicated when abutment teeth have reduced periodontal support.
- Interfere with speech.
- Not indicated with high arch palate.
Full Palatal Plate (Complete Palate Coverage) Major Connector:
Full palatal plate major connector is of three types:
- Full metal palate.
- Full acrylic palatal connector.
- Metal acrylic combination.
Indications:
- When many teeth are missing.
- Long class I edentulous condition with modification.
- When need to take support from the palate.
- In cleft palate cases.
- When remaining teeth are not sound periodontally to provide support.
Advantages:
- Advantages of metallic denture base.
- Good support and rigidity.
Disadvantages:
- Adverse tissue reaction.
- Problem in speech.
Leave a Reply