Introduction Pregnancy Tests
A pregnancy test is a test used to detect or confirm pregnancy. The basis of pregnancy tests is to determine the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the urine of a woman suspected of pregnancy. Both biological and immunological tests are available to determine the presence of hCG in the urine of the pregnant woman.
Table of Contents
Pregnancy Biological Tests
These tests are performed by using experimental animals. The biological tests for pregnancy can be performed only after 2 or 3 weeks of conception so that, the concentration of hCG in urine is sufficient to show the result.
1. Aschheim-Zondektest
- It was the first test invented for confirms-c, Op pregnancy. It depends upon the ovarian changer i-v-mature “nice caused by hCG. The immature mice do not ovulate naturally.
- Ovulation occurs only if hCG w-.i) Two mL of urine from the woman suspected of pregnancy is injected daily for two days -T ‘ creature mice.
- Five days after the injection of urine, the mice are killed. The ovaries are examined for the presence of corpora lutea (plural for corpus luteum) and hemorrhages which indicates ovulation. Ovulation is due to the presence of hCG in urine.
2. Kupperman Test
- This test is a modification of the Aschheim-Zondek test in order to save time. In this, an immature rat is used instead
- of immature mice. About 2 mL of urine is injected subcutaneously into immature rats and ovarian changes are observed after 6 hours. If the urine is injected intraperitoneally, the ovarian changes can be observed within 2 hours.
3. Friedman Test
In this test, 10 to 15 mL of urine is injected intravenously into rabbits, and ovulation is observed by examining the ovaries after 48 hours.
4. Hogben Test
In this test, about 20-30 ml of urine is concentrated and injected into the dorsal lymph sac of the South African toad, Xenopus levis. If hCG is present in the urine, it causes ovulation after 12 hours.
5. Galli-Mainini Test
- In this test, 2 mL of urine is injected into the male amphibian (toad or frog). hCG in the urine causes the expulsion of spermatozoa within 2 hours.
- The biological tests are outdated after the development of immunological tests.
Read And Learn More: Medical Physiology Notes
Disadvantages of Biological Tests
The biological tests for pregnancy are replaced by immunological tests because of several disadvantages.
- The biological test requires animals
- Tests can be performed only after 2-3 weeks of pregnancy so that a sufficient quantity of hCG is excreted in urine
- Results are not obtained quickly. One has to wait for 2-48 hours
- Tests involve tedious procedures such as sacrificing the animals.
Pregnancy Immunological Tests
The presence of hCG is also determined by using immunological techniques. The immunological tests are based on double antigen-antibody reactions. The most commonly performed immunological test is known as the Gravindex test.
Principle
The principle is to determine the agglutination of sheep RBCs coated with hCG. Latex particles could also be used instead of sheep RBCs.
Requisites
1. Antiserum from Rabbit
- Urine from a pregnant woman is collected and hCG is isolated. This hCG is injected into a rabbit.
- The rabbit develops antibodies against hCG. The antibodies are called hCG antibodies or anti-hCG. The rabbit’s blood is obtained and the serum is separated.
- The serum containing the hCG antibody is called rabbit antiserum or hCG antiserum. It is readily available in the market.
2. Red Blood Cells from Sheep
The RBCs are obtained from sheep’s blood and are coated with pure hCG obtained from the urine of the pregnant women. Nowadays, instead of sheep’s RBCs, rubberized synthetic particles called latex particles are used.
3. Urine
The urine of the woman, who needs to confirm pregnancy.
Procedure
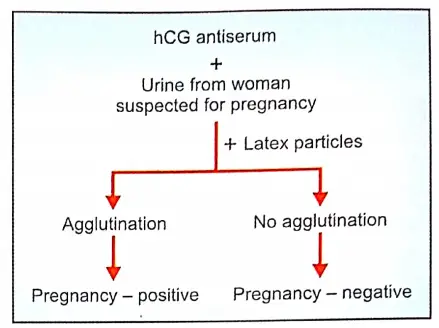
- One drop of hCG antiserum is taken on a glass slide. One drop of urine from the woman who wants to confirm pregnancy is added to this and both are mixed well.
- If the urine contains hCG, all the antibodies of antiserum are used up for agglutination of hCG molecules. The agglutination of hCG molecules by the antiserum is not visible because it is colorless
- Now, one drop of latex particles is added to this and mixed.
Observation And Result
- If the urine contains hCG, it is agglutinated by the antibodies of the antiserum, and, all the antibodies are fully used up. No free antibody is available.
- Later when latex particles are added, these particles are not agglutinated because the free antibody is not available. Thus, the absence of agglutination of latex particles confirms pregnancy.
- if it’s urine without hCG is mixed with antiserum, the an. L a.ties are freely available. When the latex particles are added. the antibodies cause agglutination of these latex particles.
- The agglutination of latex particles can be seen clearly even with the naked eye. Thus, the presence of agglutination of latex particles indicates that the woman is not pregnant.
Advantages Of Immunological Tests For Pregnancy
- Immunological tests are more accurate
- The result is obtained quickly within a few minutes
- These tests can be carried out very easily. The procedure is not cumbersome, as in the case of biological tests
- The immunological tests can be performed on the 5th day of conception. By biological methods, the tests can be performed only after 2 or 3 weeks of conception.
- concentration of hCG required for producing changes in the animals is excreted in urine only after 2 or 3 weeks of pregnancy
- Recently, available immunological tests are more sensitive and involve single-step methods. These tests can be performed even in the first few days of conception.
Leave a Reply