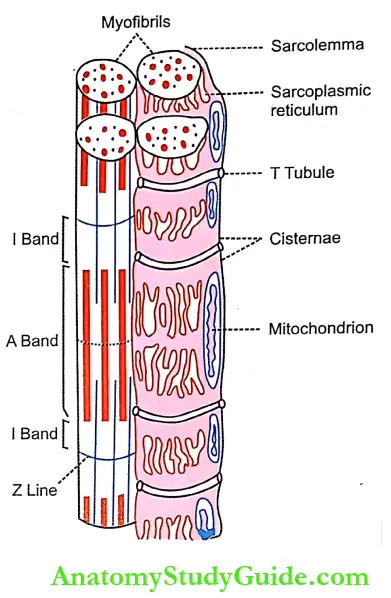
Sarcotubular System
The sarcotubular system is a system of membranous structures in the form of vesicles and tubules in the sarcoplasm of the muscle fiber. It surrounds the myofibrils embedded in the sarcoplasm.
Structures Constituting The Sarcotubular System:
The sarcotubular system is formed mainly by two types of structures:
- ‘T’ tubules
- ‘L’ tubules or sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Read And Learn More: Medical Physiology Notes
1. ‘T’ Tubules:
- ‘T’ tubules or transverse tubules are narrow tubules formed by the invagination of the sarcolemma. These tubules penetrate all the way from one side of the muscle fiber to the other side.
- That is, these tubules penetrate the muscle cell through and through. Because of their origin in the sarcolemma, the ‘T’ tubules open to the exterior of the muscle cell. Therefore, the ECF runs through its lumen.
Sarcotubular System
2. ‘L’ Tubules or Sarcoplasmic Reticulum:
- The ‘L’ tubules or longitudinal tubules are the closed tubules that run in the long axis of the muscle fiber forming sarcoplasmic reticulum) These tubules form a closed tubular system around each myofibril and do not open to the exterior like ‘T’ tubules.
- The ‘L’ tubules correspond to the endoplasmic reticulum of other cells. At regular intervals, throughout the length of the myofibrils, the ‘L’ tubules dilate to form a pair of lateral sacs called terminal cisternae.
- Each pair of terminal cisternae is in close contact with the ‘T’ tubule. The ‘T’ tubule along with the cisternae on either side is called the triad of skeletal muscle.
- In human skeletal muscle, the triads are situated at the junction between the ‘A’ band and the ‘I’ band. Calcium ions are stored in the ‘L’ tubule and the amount of calcium ions is more in cisternae.
Sarcotubular System
Functions Of Sarcotubular System:
- The function of ‘T’ Tubules:
- The ‘T’ tubules are responsible for the rapid transmission of impulses in the form of action potential from the sarcolemma to the myofibrils. When the muscle is stimulated, the action potential develops in the sarcolemma and spreads through it.
- Since the ‘T’ tubules are the continuation of the sarcolemma, the action potential passes through them and reaches the interior of the muscle fiber rapidly.
- The function of ‘L’ Tubules:
- The ‘L’ tubules store a large quantity of calcium ions. When the action potential reaches the cisternae of the ‘L’ tubule, the calcium ions are released into the sarcoplasm.
- The calcium ions trigger the processes involved in the contraction of the muscle. The process by which the calcium ions cause the contraction of the muscle is called excitation-contraction coupling.
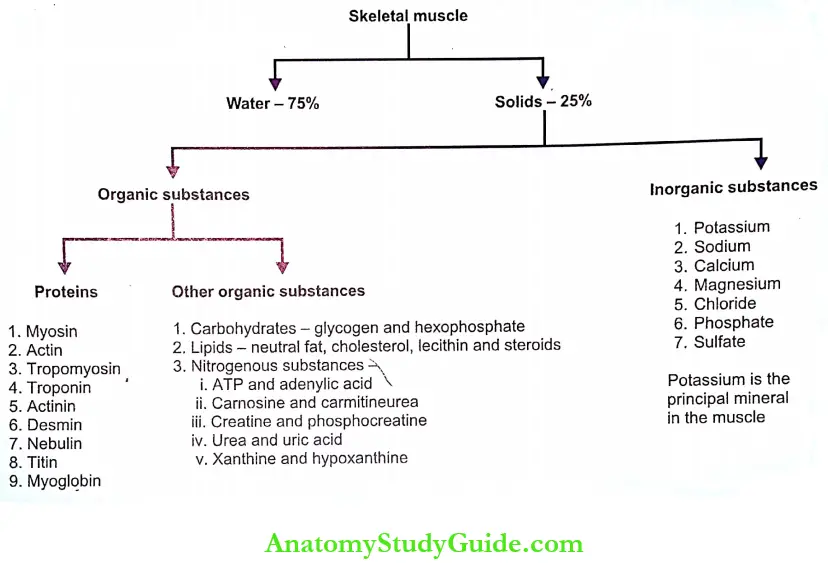
- Composition Of Muscle:
- The skeletal muscle is formed by 75% of water and 25% of solids. Solids are 20% of proteins and 5% of organic substances other than proteins and inorganic sub- stances.
- Among the proteins, the first eight proteins are already described in this chapter. Myoglobin is present in sarcoplasm. It is also called my hemoglobin. Its function is similar to that of hemoglobin, that is, to carry oxygen. It is a conjugated protein with a molecular weight of 17,000.
Leave a Reply