Assessment Of Cooperative Ability Introduction
A complete case history is obtained from the patient or the parent. It gives the background details of the patient. The cooperative ability of the child is the ability to comply with the dentist’s instructions to allow effective treatment.
Table of Contents
It is assessed with the help of the child’s baseline anxiety, emotional maturity and cognitive ability. The behaviour management strategy to be adopted during treatment depends on the cooperative ability of the child.
Read And Learn More: Paediatric Dentistry Notes
The following methods are used to assess the level of cooperation expected from the child during treatment:
- Behaviour rating scales
- Psychometric measures
- Physiological tests
- Projection techniques
The advantages of assessing the cooperative ability of the child are as follows:
- Highly anxious or excited children can be identified and more stress can be laid on multisensory communication and behaviour shaping.
- Earlier painful dental experiences of children can be identified and desensitisation can be emphasised in such cases.
- Longer appointments can be scheduled for children who are relaxed and confident to face dental operatory procedures.
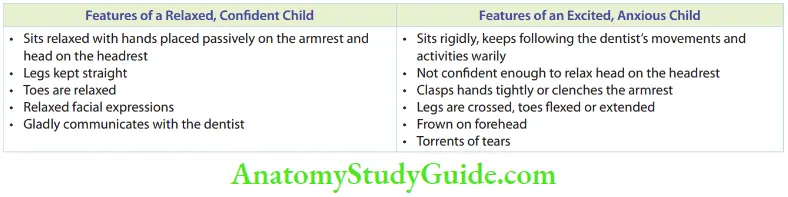
The table Enumerates the differences between a relaxed and confident child and an excited and anxious child.
Behaviour Rating Scales
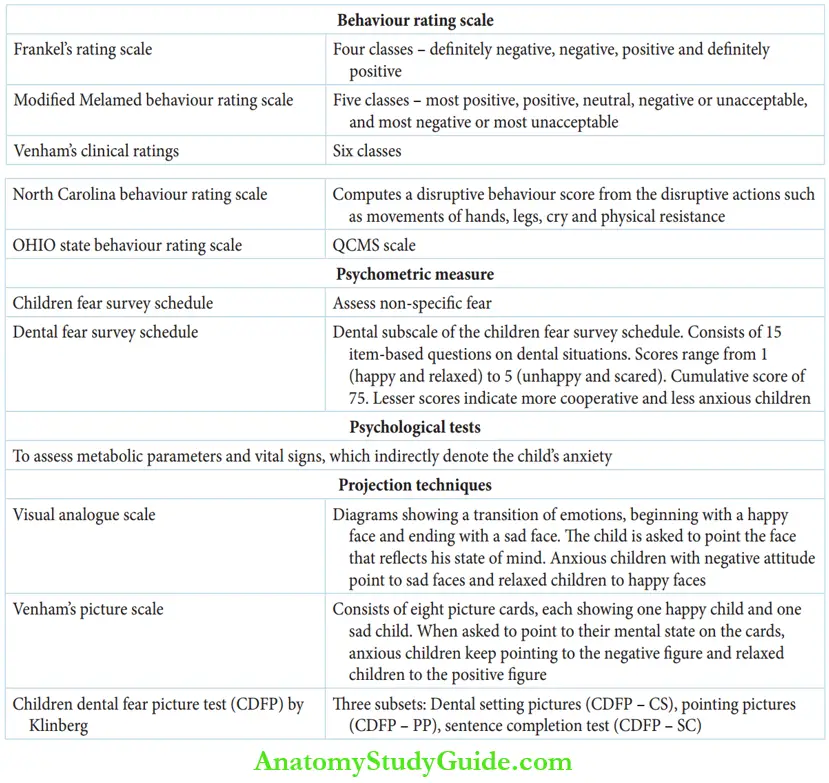
There are many behaviour rating scales of which Frankel’s behaviour rating scale is more commonly followed in dentistry. Rating scales are based on the observation of the behaviour of the child at the dental operatory.
- Frankel’S Behaviour Rating Scale Frankel’s behaviour rating scale consists of four categories. This is a simple rating procedure that can be easily applied by beginners. Each appointment of the child can be rated and a behaviour curve can be recorded. The table gives Frankel’s rating and the corresponding dental behaviour of the child.
 The other behaviour scales used less frequently are as follows:
The other behaviour scales used less frequently are as follows:
- Modified Melamed behaviour rating scale: There are five classes of behaviour expressions according to Melamed. These classes include most positive, positive, neutral, negative or unacceptable, and most negative or most unacceptable.
- Venham’s clinical ratings: There are six categories of child behaviour presentation, ranging from a relaxed child to one who is out of control and severely misbehaving. The categories are given in Table.

- North Carolina behaviour rating scale: The scale computes a disruptive behaviour score from disruptive actions such as the following:
-
-
- Movements of hands
- Movements of legs
- Crying
- Verbal and physical resistance
-
-
- OHIO state behaviour rating scale: This customised scale is denoted as the QCMS scale where
-
-
- Q – is quiet behaviour with no movement
- C – is crying with no struggling
- M – is a movement with struggling
- S – is crying and struggling
-
Psychometric Measures
Psychometric measures describe the cooperative ability of the patient indirectly by assessing the baseline anxiety, especially in relation to a dental situation. The two methods of assessment are the children fear survey and the dental fear survey. Children fear survey assesses the general fear of a child in a nonspecific setting.
The dental fear survey correlates the fear of the child with a dental situation. It is the dental subscale of the children’s fear survey schedule. The test consists of 15 item-based questions on various dental situations faced by the child, for example dentist drilling your teeth, nurse cleaning your teeth.
The children give scores ranging from 1 (happy and relaxed) to 5 (unhappy and scared) for each of the 15 items. The cumulated score ranges from 15 to 75. Children who have scored less are expected to be more cooperative and less anxious during dental treatment.
Physiological Methods
Several metabolic parameters and vital signs indirectly denote the child’s anxiety and cooperative ability towards dental treatment. The various parameters assessed are as follows:
- Heart rate
- Respiratory rate
- Systolic blood pressure
- Peripheral oxygen perfusion by a pulse oximeter
- Diastolic blood pressure
- Expired CO2 concentration
When the child is anxious the heart rate, respiration rate and blood pressure increase demonstrably. When the respiration rate increases, the depth of respiration becomes shallow.
Hence, the peripheral oxygen perfusion and expired carbon dioxide concentration decrease considerably. Retrospectively, when these physiological parameters are identified, the child is described to be anxious.
The magnitude of the increase or decrease of these physiological parameters indicates the quantum of anxiety of the child.
Projection tasks
It is suggested that the fear of a child will be displayed by certain tasks. The child in a dental operatory is asked to perform tasks such as pointing to pictures, drawing figures, telling stories and so on. This can be an indirect but reliable indicator of the child’s cooperative ability.
The most commonly suggested projection tasks are discussed in the following text.
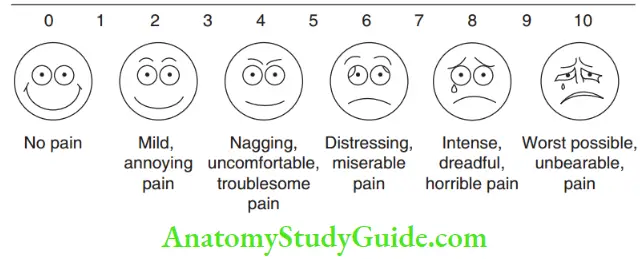
- Visual Analogue Scale Wewers and Lowe (1990) brought an elaborate description on the use of the visual analogue scale. The visual analogue chart shown in Figure 16.1 was given by Wewers and Lowe in 1990. It is shown to the child in the dental operatory so as to recognise the behaviour expected from the child. The child will point out to the figure that reflects his mind. Children with higher fear, anxiety and negative attitude are expected to point towards the sad faces. Confident and relaxed children point towards the happy face. The corresponding scores indicate the child’s cooperative ability.
- Venham’S Picture Test Venham’s picture test consists of eight picture cards, as shown in the figure. Each picture card depicts two children of which one is happy and relaxed and the other is sad, crying or withdrawn. The patient is asked to point to one child in each card. Every child will choose a picture that depicts his/her mental state. Anxious children keep pointing to the negative figure in the picture cards while relaxed children keep pointing to the positive figure. The positive figures have green faces while the negative figures have red faces for easy understanding. The original representation by Venham was not colour coded so as to eliminate preferential bias in children.

- Children’s Dental Fear Picture Test Children’s dental fear picture test (CDFP) was conceptualised by Klinberg in 1994. It consists of three subtests, which are as follows:
- Dental setting pictures (CDFP – CS): It consists of 15 cartoon cards depicting animals undergoing dental treatment. The cartoons are shown to the child and the mental frame is assessed by asking the child to score the cartoon from 1 (relaxed) to 5 (excited).
- Pointing pictures (CDFP – PP): It consists of five sets of pictures for males and females. Each picture set depicts a relaxed child and a nervous child in different dental situations such as
- Before going to the dentist
- During examination by the dentist
- While receiving an injection
- While teeth are being drilled by the dentist
- Crying in bed dreaming about the dentist
- The child is asked to point out to a picture in each of the sets. This reflects the child’s mind.
- Sentence completion test (CDFP – SC): Fifteen incomplete sentences pertaining to dental treatment are put forward and the child is asked to complete them. The answers may possibly reflect the relaxed/ excited state of the mind of the child.
Summary
- The ability of the child to comply with the dentist’s instructions and allow effective dental treatment to be imparted is termed cooperative ability.
- The assessment of cooperative ability helps in identifying the following:

- To assess metabolic parameters and vital signs, which indirectly denote the child’s anxiety
- To assess metabolic parameters and vital signs, which indirectly denote the child’s anxiety
Leave a Reply