Choledochal Cyst
It is a congenital cyst occurring in the CBD due to partial or complete weakness of the wall of the CBD. Majority of cases manifest by 1-2 years of age.
Table of Contents
Choledochal Cyst Classification- Recent advances: Type 6—cystic dilatation of cystic duct.
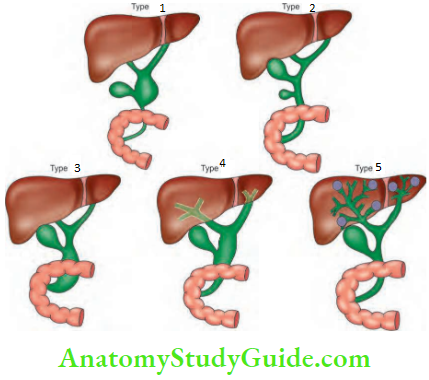
Choledochal Cyst Clinical Features
- Age: Majority of cases manifest in children within 1-2 years of age. It can also present in adults.
- More common in females—4:1.
- Abdominal distension can be due to a large cyst. The cyst can be palpated per abdomen in the right hypochondrium.
- Slow progressive jaundice, recurrent attacks with abdominal pain and pyrexia.
Choledochal Cyst Investigations
- USG will confirm presence of abnormal cyst. It is usually unilocular cyst.
- MRC: It will define the relation between lower end of the bile duct and pancreatic duct to know basic anatomy.
- CT is also useful to know intrahepatic and extra- hepatic dilatation.
- ERCP may be done but it will not give any more information than MRC.
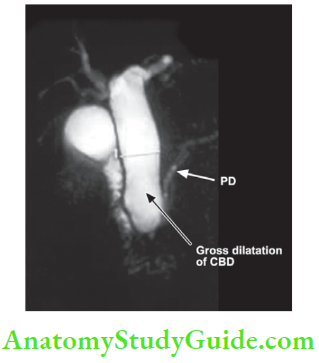
Choledochal Cyst Treatment: This anomaly is premalignant. Change to carcinoma is a well-recognised complication and it carries poor prognosis. Hence, excision of the cyst and reconstruction is the treatment of choice
- Type 1: Excision of the cyst followed by Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy.
- Type 2: Excision of the diverticulum with suturing of CBD.
- Type 3: Endoscopic sphincterotomy is adequate (choledochocele).
- Type 4: They are difficult to treat. Due to recurrent cholangitis, if total excision is not possible due to adhesions between the cyst and portal vein, posterior wall of the cyst can be left behind, after removal of mucosa. This is described as Lilly’s technique.
- Type 5 will be described later.
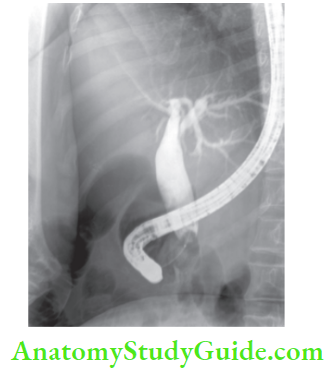
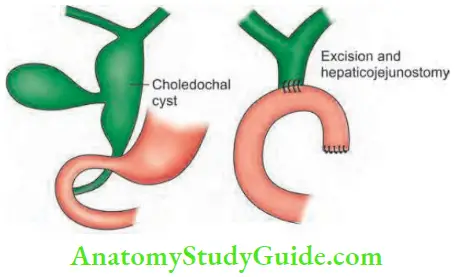
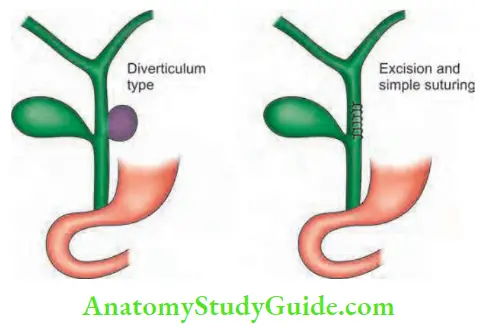
Choledochal Cyst Complications
- Recurrent cholangitis with high-grade fever, resulting in biliary cirrhosis.
- Rupture of the cyst resulting in biliary peritonitis.
- CBD stones
- Carcinoma in the cyst (25-30% of cases). It is a cholangiocarcinoma common in types 1 and 5.
Caroli’s Disease
It is a hereditary condition wherein there is dilatation of intrahepatic ducts with stenotic segments in between. Multiple, irregular saccular dilatations are characteristic. It is also an example of type 5 choledochal cyst. Two types:
- Simple: Presents later with abdominal pain and sepsis.
- Periportal: It occurs in childhood, presents as recurrent cholangitis.
- Diagnosed by ultrasound and CT scan. MRI and ERCP are other investigations.
- Associated lesions are given.
- Congenital hepatic fibrosis
- Medullary sponge kidney
- Polycystic liver
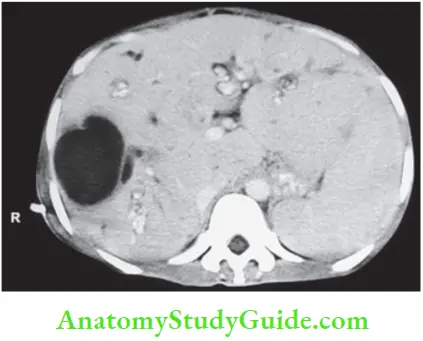
Caroli’s Disease Complications
- Cholangitis: It occurs due to constant obstruction.
- Stones: Obstruction and stasis precipitate stone formation.
- Biliary cirrhosis
- Cholangiocarcinoma
Caroli’s Disease Treatment: Hepatectomy, liver transplantation.
Leave a Reply