Classification Of Special Children Introduction
Every child is unique. Children are emotionally and physically immature and cannot independently meet their sociocultural expectations.
Table of Contents
They are primarily dependent upon their parents/primary caretakers. They need care and attention to lead life till they grow into adults who are mature and independent.
Some children may require additional attention or extra care for fulfil their basic necessities owing to their cognitive impairment, visual or other sensory impairment or any other medical condition.
They are called children with special care needs. They are also referred to as differently-abled children.
| Body Fluids | Muscle Physiology | Digestive System |
| Endocrinology | Face Anatomy | Neck Anatomy |
| Lower Limb | Upper Limb | Nervous System |
Though terms such as disabled child, retarded child or handicapped child appear in literature, the usage of these terms is not recommended.
WHO describes a child with special care needs as one who, over an appreciable period of time, is prevented by physical or mental conditions from full participation in the normal activities of their age groups including those of a social, recreational, educational and vocational nature.
This description clearly identifies children who may be classified as those with special care needs.
A child with a fractured arm resting at home is not considered a child with special care needs.
His physical or medical condition shall not prolong for an ‘appreciable’ length of time; the period of rest may probably extend for a month only.
A child with a deformed toe is not classified as a special child as long as his physical deformity does not prevent him from full participation in the normal activities of his/her age group.
Classification:
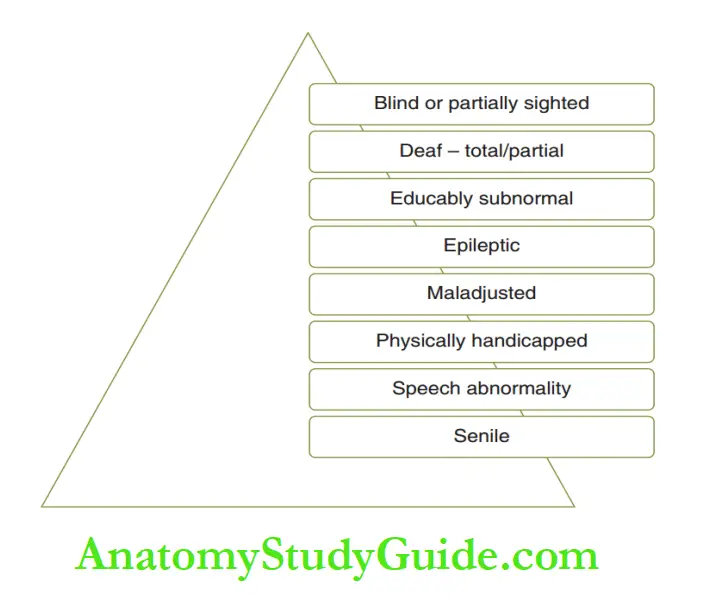
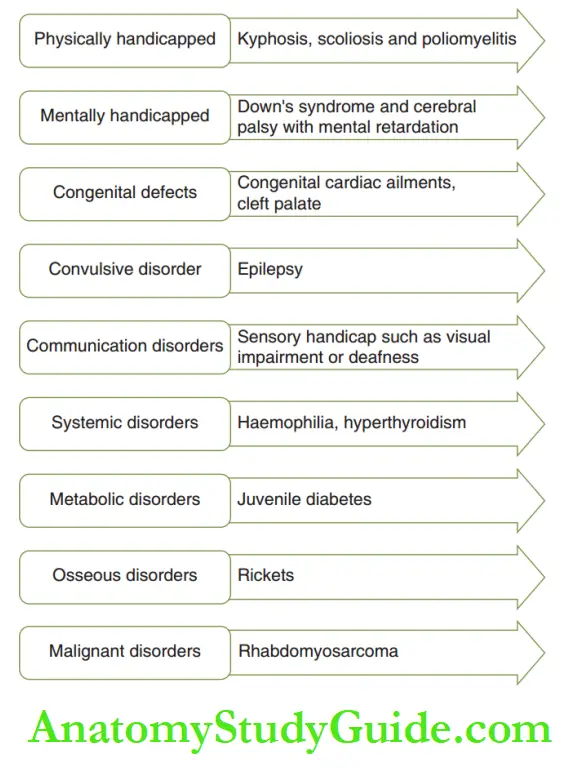
Special children have been classified by Frank al Winters in 1974, Agerholm in 1975 and Nowak in 1976.
These classifications are depicted, respectively.
Special children are broadly classified as congenitally or developmentally disabled and medically compromised children.
The behaviour management of such children in the dental clinic, their special attention requirement and treatment requirement.
Objectives Of Management Of Special Children
Apart from the core objectives of paediatric dentistry, the objectives of dental management of special children focus on preventive dentistry.
These objectives are as follows:
1. Oral hygiene measure: Maintenance of good oral hygiene is the most efficient mode to prevent dental diseases.
Meticulous tooth brushing is essential for maintaining oral hygiene.
If the child cannot be trained to perform or cannot perform due to cognitive or physical impairment, then the parent or Frank al Winter’s classification of special children into eight categories.
Agerholm’s classification of handicap conditions. primary caretaker is trained to brush the child’s teeth meticulously.
The following instructions are given to the parent or primary caretaker while brushing the child’s teeth:
The importance of maintaining the stability of the child’s head while brushing is taught.
The parent or primary caretaker has to stand behind the child at 10–12’o clock position while brushing.
The child and the caretaker have to be seated, the care taker half feet higher than the child.

2. Diet counselling: The diet prescribed for the child should contain low sugar and high fire content. Cariogenic stuff sticky solid food and frequent snacking should be avoided.
3. Fluoride exposure: As a part of the home fluoride programme, low-fluoride (paediatric) toothpaste should be advised while brushing. Annual topical fluoride application is recommended for caries prevention.
4. Sealant application: Due to enhanced cariogenic susceptibility, special children require specific protection on permanent molars.
Pit and fissure sealant application on first molars between 6½ and 7½ years of age and on second molars between 12 and 13 years of age would be appropriate.
Summary
1. Children who require extra care and additional attention to fulfil their basic needs due to their cognitive, or sensory
impairment or other medical conditions are referred to as children with special needs.
2. Classification of children with special needs was given by Frank, Agerholm and Novak.
3. Dental management of these children includes the following:
- Emphasis on oral hygiene measures
- Diet counselling
- Fluoride exposure
- Pit and fissure sealant application
Leave a Reply