Paediatric Operative Dentistry An Overview
Operative dentistry is the art and science of the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of the defects of teeth that do not require full-coverage restorations for correction.
Table of Contents
Such treatment should result in the restoration of proper tooth form, function and aesthetics while maintaining the physiological integrity of the teeth in a harmonious relationship with the adjacent hard and soft tissues.
All of which should enhance the general health and well-being of the patient.
Read And Learn More: Paediatric Dentistry Notes
Over the decades, operative dentistry (synonymous with restorative dentistry and conservative dentistry) has been dynamic to include a multitude of changes with improved restorative materials and operative strategies.
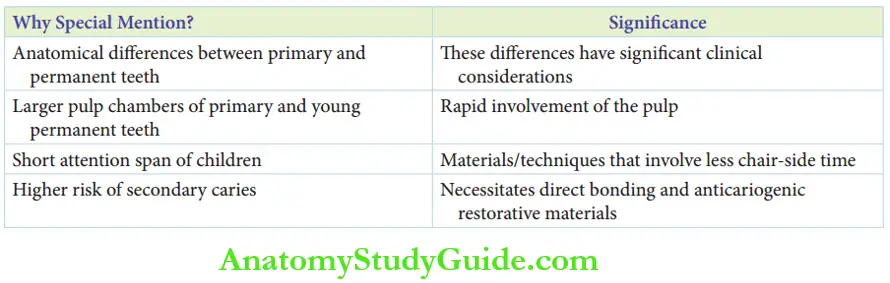
Operative dentistry for children, or paediatric operative dentistry, requires special mention due to the following aspects:
- The anatomical differences between primary and permanent teeth have significant clinical considerations. These are listed in Table.
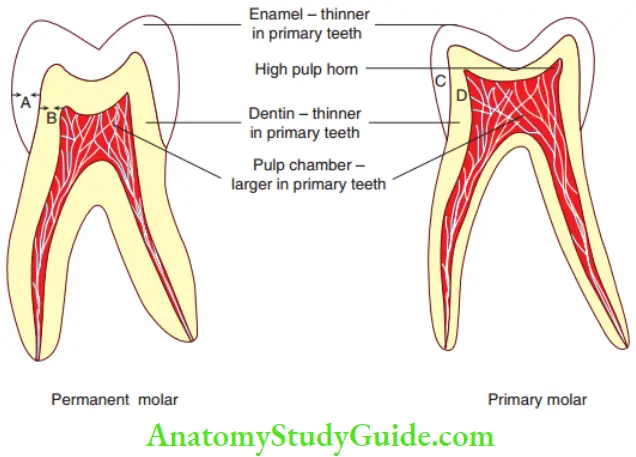
- Primary teeth and young permanent teeth have large pulp chambers. This leads to the rapid involvement of pulp with caries progression.
- Restorative methods or materials used for restoration in children should require less chairside time.
- This is because children have a very short attention span beyond which they may not cooperate with the treatment.
- The risk of secondary caries is higher in children owing to poor oral hygiene and dietary habits.
- So direct bonding (negligible microleakage) and fluoride-releasing (anti-cariogenic effect) restorative materials are preferred to other materials with good mechanical properties.
Paediatric Dentistry
Anatomical Features and Clinical Considerations of Primary Teeth
Anatomical Differences Between Primary And Permanent Dentition
The anatomical features of the primary teeth and the corresponding clinical considerations in paediatric operative dentistry are discussed in Table.
Paediatric Dentistry
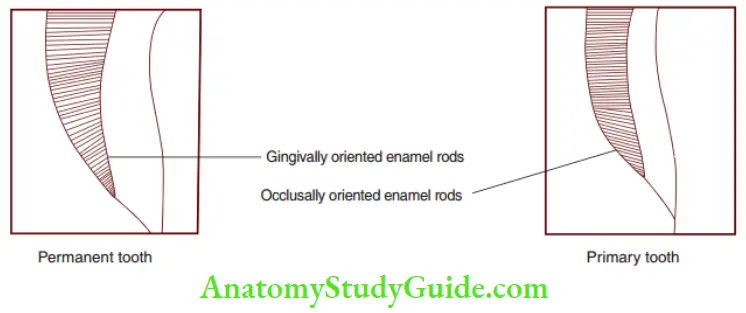
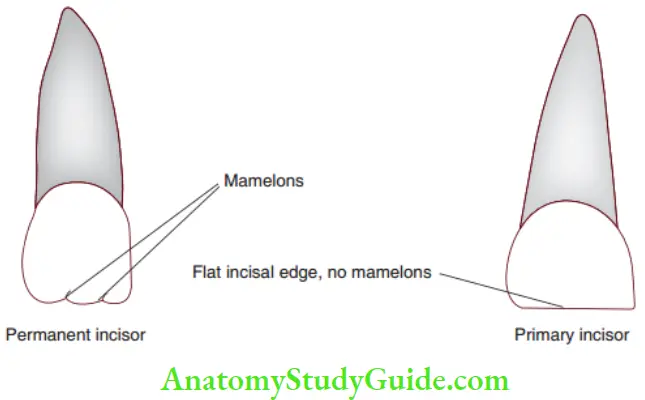
Figures depict the anatomical differences between the primary and permanent teeth
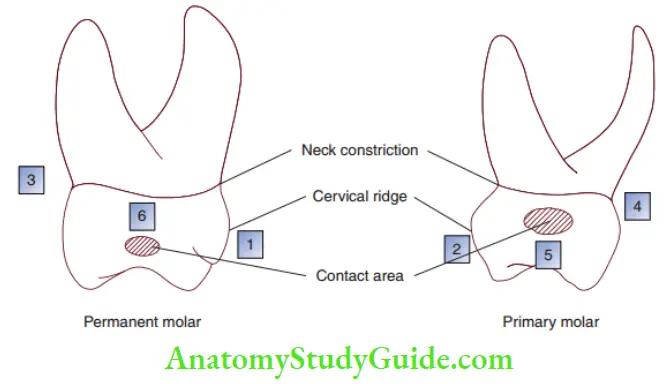
- 1 and 2: More pronounced cervical ridge in primary molar than in permanent molar.
- 3 and 4: Bulbous tooth with a sharp neck constriction in primary molar than in permanent molar.
- 5: Broad and flat contact area situated more gingivally in primary molar (shaded area).
- 6: Contact area situated more occlusally in permanent molar (shaded area).
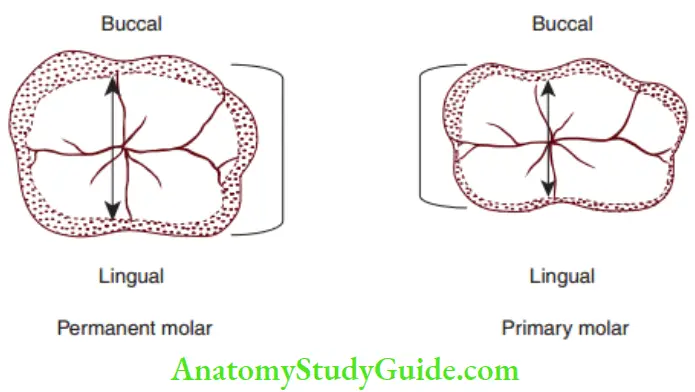
Paediatric Operative Dentistry Summary
1. ‘Paediatric’ operative dentistry requires special mention because of the following reasons:
2. The anatomical features of the primary teeth and the corresponding clinical considerations in paediatric operative dentistry are discussed in Table.
Leave a Reply