Steroids And Related Compounds Introduction
Steroids are a large class of tetracyclic terpene containing 17 carbons with specified arrangement of four fused ring, which are widely distributed in animals and plants. All steroids are made in cells either from Cholesterol and Lanosterol (animal and fungi) or from Sitosterol (plants). There are four classes of steroids:
Table of Contents
- Steroidal hormones
- Adrenocorticoids
- Bile acids
- Vitamin D
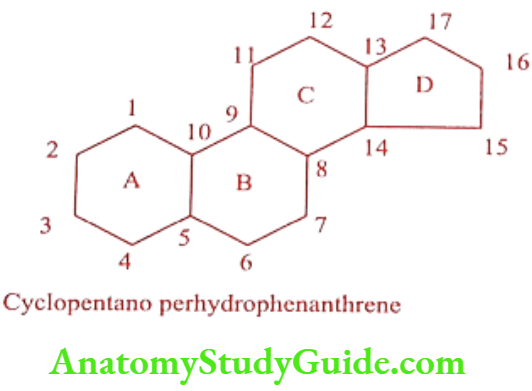
Sterols possess a common basic structure cyclopentano perhydrophenanthrene (Sterane) nucleus. In addition they contain two angular methyl groups (CH3) at C18 and C19 attached to C10 and C13 respectively. There is a presence of oxygen-containing functional group at C3 followed by with or without carbon side chain at C17.
All the steroids, on dehydrogenation with selenium at 360°C yield Diel’s hydrocarbon, whereas at 420°C, the steroid gives mainly chrysene and a small quantity of picene.
Structure and Stereochemistry
The ring A, B and C are 6- 6-membered, whereas ring D is 5-membered. The ring A/B system can occur either as cis or trans. The rings B/C are fused transform only in natural steroids, whereas rings C/D are always trans-fused. It exists six centers of 64 stereo isomeric forms are asymmetry (Cs, C8, C9, C10, C13 and C14), thus 26 theoretically possible. Depends upon number of substitutions, the center of asymmetry go up to eight and the number of stereoisomers to 256.
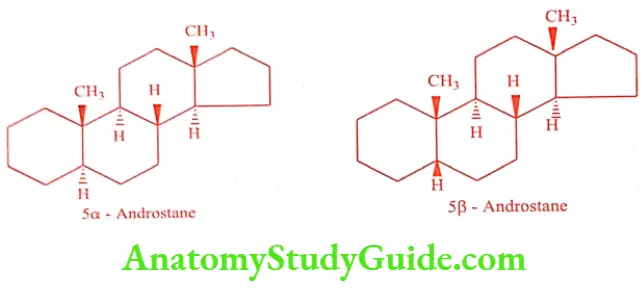
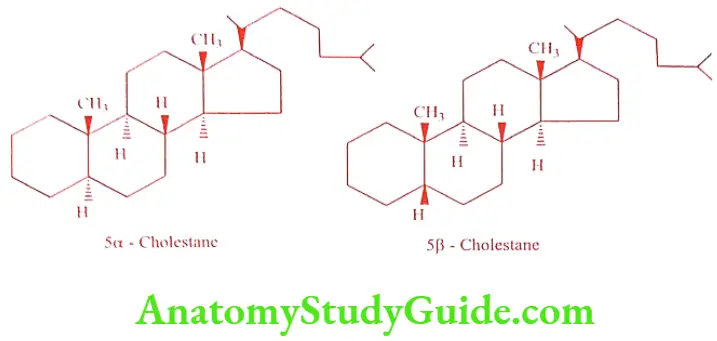
Androstane is a simple parent hydrocarbon consists of 19 carbons present in male sex hormone Testosterone. The structure of 5a-androstane and 5ẞ-androstane is given below. In 5a-androstane ring A/B are trans-fused, whereas in 5ẞ-androstane ring A/B are cis fused. In both rings B/C and C/D are trans fused.
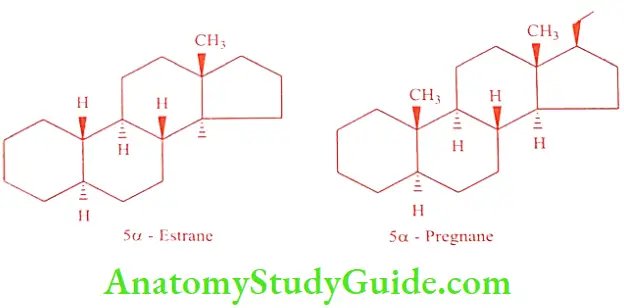
Estrane is the basic structure present in estrogens, and has 18 carbon skeleton structures, without angular methyl group at C10. Pregnane hydrocarbon is made up of 21 carbons, which is present in progesterone and adrenocortical hormones. Two carbon side chain attached to the carbon at C17-
Nomenclature
A group of hydrogen at particular carbon, shown by thick line, indicated above the plane of the nucleus is designated as beta (B) configuration and shown by dotted line indicated below the plane and is termed as alpha (a) configuration. If the configuration of the substituent is unknown its bond to the nucleus is drawn as a wavy line and this is indicated by E(xi) in the name. Wherever possible, the name of the steroid should specify stereo chemical configuration.
The configuration of the H at Cs is always indicated in the name. If the double bond is not present between sequentially numbered carbons in such cases both the carbons are indicated in the name. When a methyl group is missing from the side chain, which is indicated by prefix “nor” with the number of the carbon atom, which has disappeared.
The symbol A is often used to designate a C = C bond in a sterol. If the double bond is between C4 and Cs the compound is referred as ▲ steroid. If the double bond is between the position Cs and C10, then the compound is designated as ▲5(10) steroid.
When a ring has contracted or enlarged, indicated by prefixes ‘nor’ or ‘homo’ respectively, proceeded by a small capital letter indicating the ring affected. When ring- fission has occurred, this is indicated by the numbers showing the position of the bond broken, followed by the prefix ‘seco’. The prefix ‘cyclo’ is used to indicate the three- member ring.
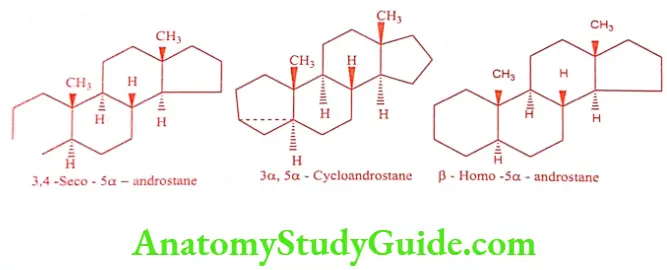
Compounds that are derived from 5a-chloestane belongs to the allo-series, whereas compounds derived from 5ẞ-cholestane (coprostane) belongs to the normal series.
Steroid Biosynthesis
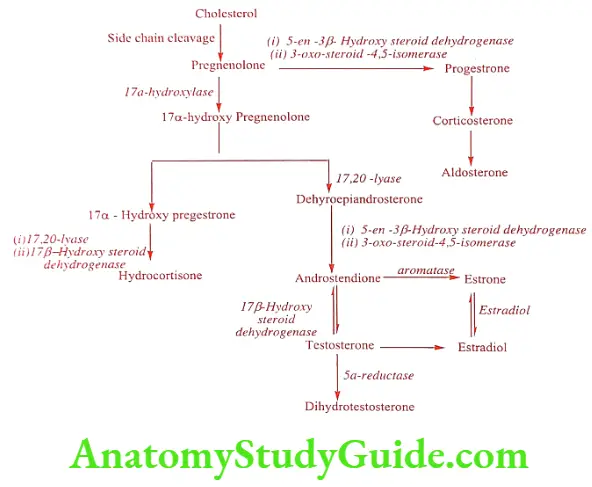
Steroidal hormones are biosynthesized from Cholesterol in mammals. Cholesterol is stored in endocrine tissue and is converted into Pregnenolone serves as a precursor in the formation of adrenocorticoids and sex hormones. The main routes of biosynthesis.
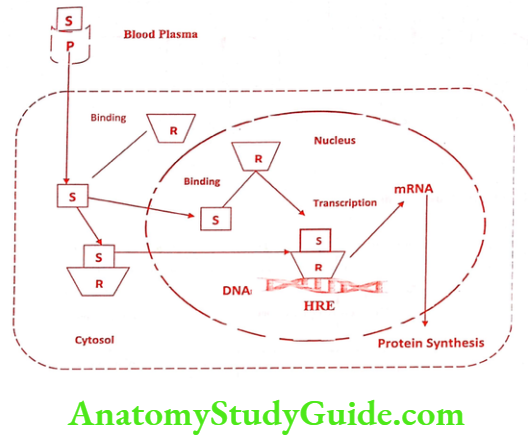
Mechanism of Action
The steroidal hormones (S) act on the target cell to regulate gene expression and protein biosynthesis via the formation of steroid-receptor complex. In addition to structural similarity adrenocorticoids, estrogen, progestin, and androgens share a common mode of action. Steroidal hormones travel in the blood and attach to the protein carriers (P).
When it reaches the target cell, they enter in the cell through diffusion. Some steroidal hormones bind to the specific protein in the cytoplasm and move as a hormone receptor complex into the nucleus. Others travel directly into the nucleus before encountering their receptor (R) protein or bind to the binding sites in the nucleus. When the hormone binds to the receptor, a characteristic series of event occurs
- The binding initiates conformational changes in the receptor known as receptor activation. The major consequence of receptor activation is that the receptor becomes competent to bind DNA.
- Activated receptor binds to particular region of the DNA, referred as “hormone-responsive element” and promotes the hormone-responsive gene.
- This stimulates transcription from the gene to produce mRNA.
- Finally, the elevated level of mRNA leads to an increase in protein synthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum. These proteins include enzymes, receptors and secreted factors that results in steroidal hormone response regulating cell function, growth etc.,
Sex Hormones
Sex hormones are usually classified as follows
- Androgens (Male sex hormones)
- Estrogens (Female or Follicular hormones)
- Gestogens (Corpus luteum hormones)
Androgens
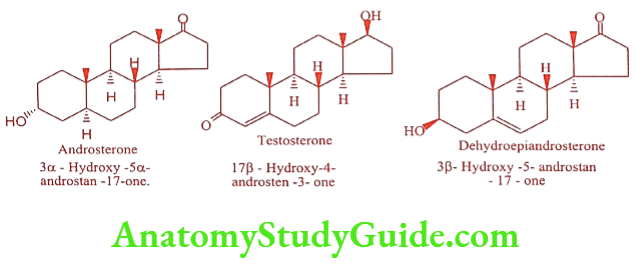
The principle class of male sex steroidal hormones is androgens. Androgens are the substances that cause development of secondary sex characters in the castrated male. The first androgen Androsterone was isolated from male urine. The second and third such hormones from males were dehydroepiandrosterone and Testosterone respectively.
Androgen comprises a group of steroids that produces biological effects of primary and secondary sex characteristics. Androgens are male sex hormones produced mainly by the testes, ovary, and adrenal cortex. They possess potent anabolic and androgenic properties. Testosterone is 10 times more potent than Androsterone.
Classification
Androgens are classified as follows.
- Natural androgens :
- Example: Testosterone, Dihydrotestosterone, Dehydroepiandrosterone.
- Synthetic androgens :
- Example: Methyltestosterone, Fluoxymesterone, Testosterone undecanoate.
- Anabolic agents :
- Example: Oxymetholone, Stanozolol, Danazol, Nandrolone.
Natural Androgens
Testosterone (Testonova, Sustrone)
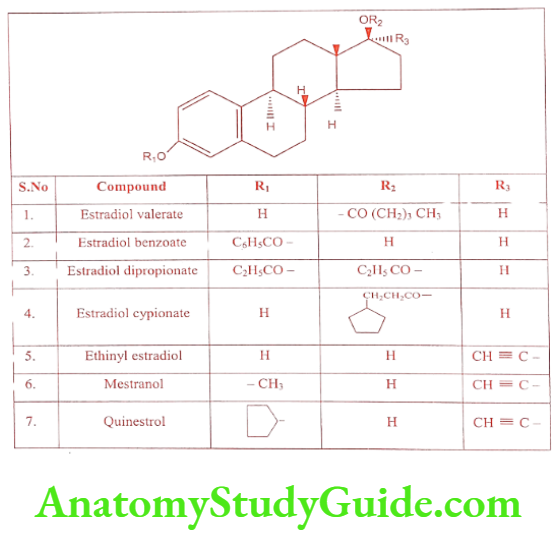
It is naturally occurring androgen in men. Testosterone deficiency (male hypogonadism) is the inability of the testes to produce sufficient testosterone to maintain sexual function, muscle strength, bone mineral density, and fertility (spermatogenesis). It is available in a transdermal delivery system, a gel formulation, and as implantable pellets, It is only weakly active orally, but its esters exhibit prolonged or delayed action, thus reducing the frequency of injection. This may be due to slow hydrolysis to limited solubility or to slow uptake from the site of injection. The Testosterone esters used in medicine are given in the table.
ADR: Fluid and electrolyte retention, increased vascularity of the skin, hypercalcemia, and impaired glucose tolerance.
Dose: 50 to 400mg every 2 to 4 weeks,
Use: Testosterone and structurally related androgens are used to treat male hypogonadism, Klinefelter’s syndrome (chromosomal abnormalities resulting in testicular dysfunction), aplastic anemia, and as antiandrogens.
Synthetic Androgens
Methyltestosterone (Android, Trstred, Virilon)
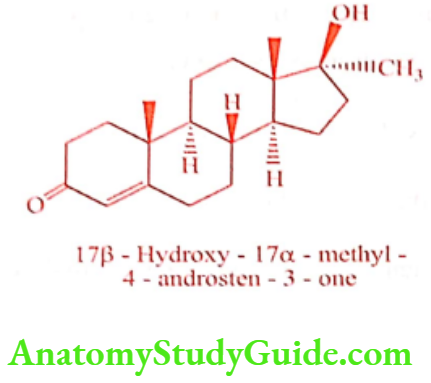
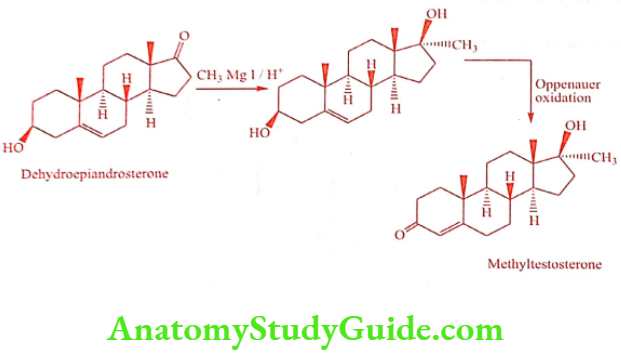
Introduction of the 17α -methyl group into Testosterone gives Methyl testosterone, which is approximately half of the androgenic activity, but orally active as an anabolic agent. More active when given sublingually. The alkylated oral androgen is hepatotoxic.
Synthesis
ADR: Headache, hair loss, dizziness, rash, anxiety, edema hepatic disturbances jaundice, and death occur particularly in high doses often used by athletes.
Dose: 10 to 50mg orally once a day.
Use: It is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms and also to treat breast cancer.
Fluoxymesterone (Halotestin)
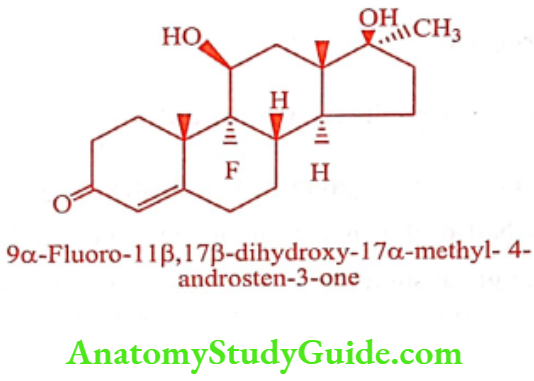
Fluoxymesterone is an analog of 17α-methyl testosterone, obtained by substituting the fluoro group in 9α – position. It is 20 times more anabolic and 10 times the androgenic activity of 17α – methyl testosterone.
ADR: Sodium and water retention leads to edema.
Dose: 10 to 40mg/day in 3 or 4 divided doses.
Use: It is used in the treatment of breast neoplasms, male hypogonadism, and delayed puberty.
Anabolic Agents
Oxymetholone (Adroyd)
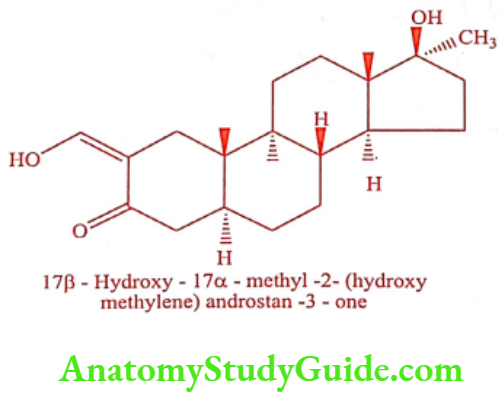
ADR: Nausea, bloating, and acne.
Dose: 5 to 10mg once daily.
Use: It is used for the treatment of osteoporosis and various types of anemia resulting from bone marrow failure.
Stanozolol (Menabol)
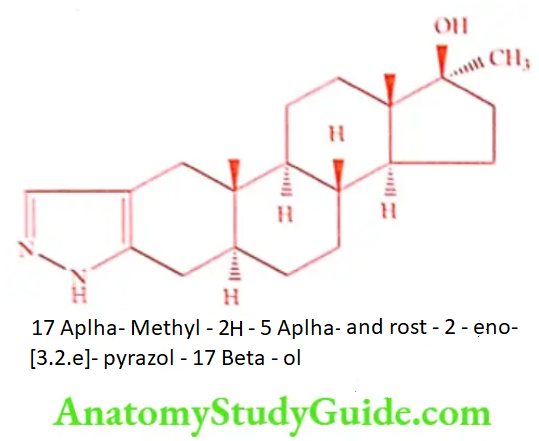
ADR: Peliosis hepatis, cholestatic jaundice, impotence and priapism.
Dose: Initially, 2.5 to 10mg daily, reduced according to response.
Use: It has strong anabolic activity used for weight gain.
Danazol (Danogen, Zendol)
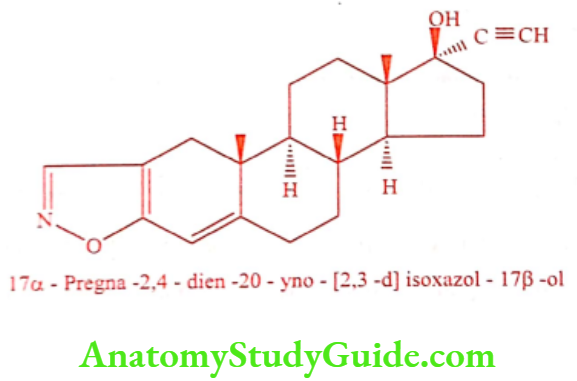
ADR: Weight gain, edema, sweating, acne and flushing.
Dose: Initially, 100 to 400mg daily in two divided doses.
Use: It has weak androgenic activity and no progesterone or estrogenic effect. It is used in the treatment of endometriosis.
Nandrolone (Nandrobol, Nisdrol)
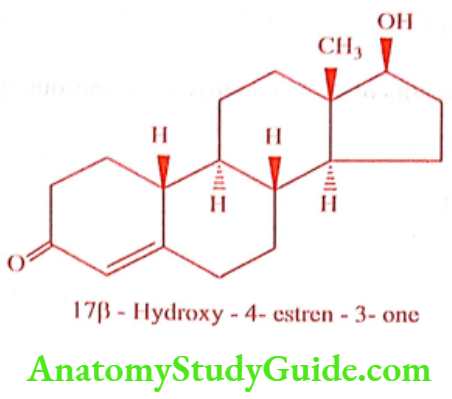
ADR: Acne, gynaecomastia, bladder irritability and priapism.
Dose: 25 to 100mg once every 3 to 4 weeks.
Use: It is mainly used in the treatment of chronic wasting diseases and osteoporosis. It has long duration of action. It is used in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer in Women.
Structure-Activity Relationship
- Steroidal skeleton cyclopentane perhydro phenanthrene ring is essential for activity.
- Ring expansion by inserting a methyl group and ring contraction by removing a methyl group, in any ring in the steroidal nucleus reduces or destroys the androgenic activity.
- The presence of oxygen functionalities (OH or Keto group) in the 3rd position enhances the activity.
- The 17ẞ-OH group is important for binding with the receptor.
- The presence of methyl group in the 17th position prevents the metabolic change in that position and renders the compound orally active
- Example: Methyl testosterone).
- Increasing the length of the alkyl chain decreases the activity.
- Except in position 4 or 6 substitutions of halogen in any other position decrease the activity
- Example: Fluoxymesterone
- Alkylation in 1, 2, 7, and 18 position of androstanolone increases anabolic activity.
- Example: Oxymetholone)
- Removal of methyl group at 19th position, reduction of 5α-position, and replacement of carbon at 2nd position with oxygen
- Example: Azasteroids and ox asteroids) are all the structural changes that tend to increase anabolic activity.
Estrogens
Estrogens are mainly concerned with the development and maintenance of secondary female sex characteristics. It is also needed for the maintenance of pregnancy and has an anabolic effect on protein metabolism and water retention. They are found in humans and other mammals.
Classification
Estrogens are classified as follows:
- Natural estrogens:
- Example: Estradiol, Estrone, Estriol.
- Semi-synthetic estrogens:
- Example: Ethinylestradiol, Mestranol.
- Synthetic estrogens:
- Example: Stilboestrol, Dienoestrol, Hexoestrol, Benzoestrol, Chlortrianisene, Methallenoestril.
Natural Estrogens
The three main major estrogens in human being are Estrone, Estradiol, and Estriol. Estrone and Estriol are metabolite of estradiol in vivo. Estrone is about 1/3rd active as Estradiol and Estriol is about 1/6th as active as Estradiol.
Estrone
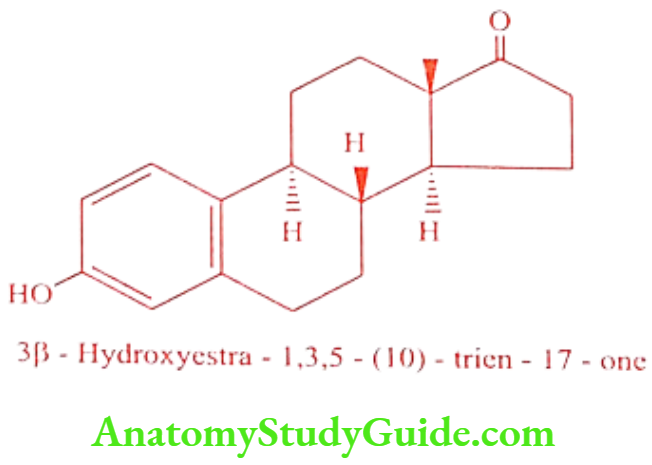
ADR: Peripheral edema, blotting, headache, and amenorrhea.
Dose: 0.1 to 0.5mg i.m 2 to 3 times a week for menopause. 2 to 4mg i.m 2 to 3 times a week for prostate cancer.
Use: It is mainly used for the treatment of delayed onset of puberty, management of menopausal syndrome, and prostate cancer.
Estriol (Evalon)
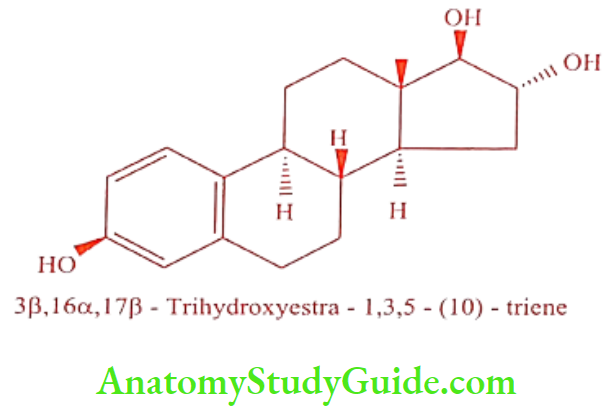
ADR: Suppression of libido and gynecomastia.
Dose: Initially 4 to 8mg/day, maintenance dose in menopause 1.2 mg/day orally.
Use: It is used mainly in oral contraceptives and for hormone replacement therapy in post-menopausal women.
Estradiol (Ovocyclin, Progynon)
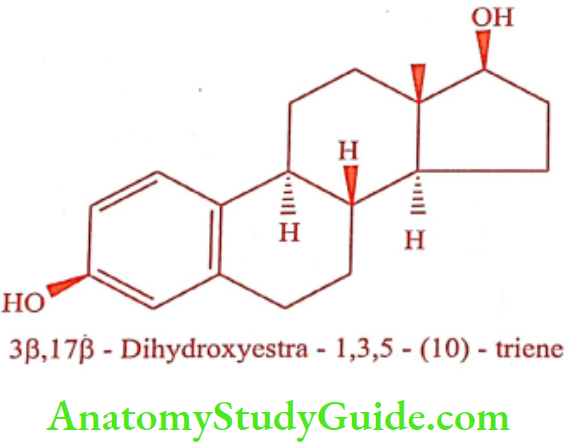
Estradiol is a potent endogenous estrogen with high potency when administered parenterally. Oral bioavailability of Estradiol is low because it undergoes oxidative metabolism by the liver. To increase the duration of action Estradiol is converted into its ester prodrug. Therapeutically useful esters of Estradiol are given in the Table. Conjugated estrogen is a mixture of the sulfate ester of Estradiol derived from Estrone
ADR: Suppression of libido, gynecomastia and risk of endometrial carcinoma.
Dose: 1 to 2mg daily in cycles of 21 days on and 7 days off or cycles of 5 days on and 2 days off.
Use: It is used mainly in oral contraceptives and for hormone replacement therapy in post-menopausal women.
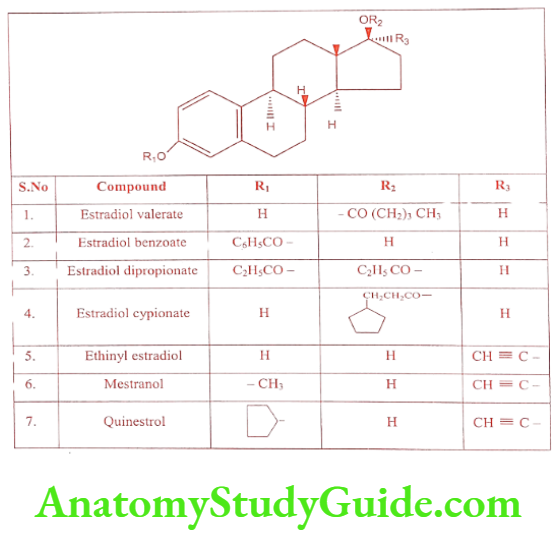
Semi-synthetic Estrogens
To increase the oral bioavailability of the estrogen the C-17th position is alkylated by inserting an alkyne group. The synthetic derivatives are several-fold more potent than the natural estrogen.
Ethinylestradiol (Lynoral, Progynon)
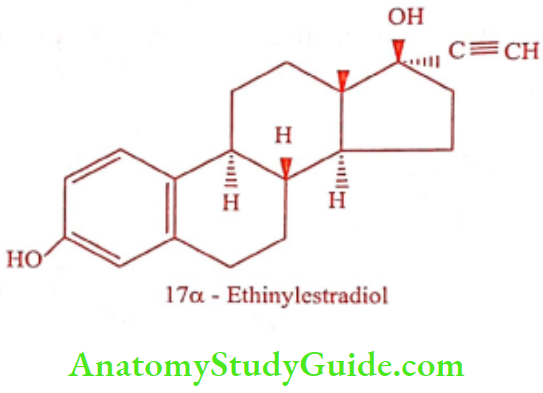
Synthesis
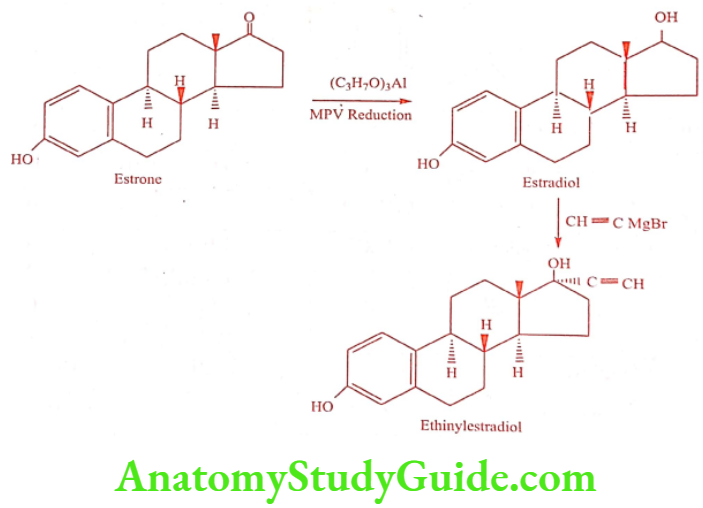
ADR: Hypertension, edema, dizziness, headache and vomiting.
Dose: In menopausal women 10 to 20μg daily.
Use: It is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms and carcinoma of the prostate.
Mestranol (Ovulen)
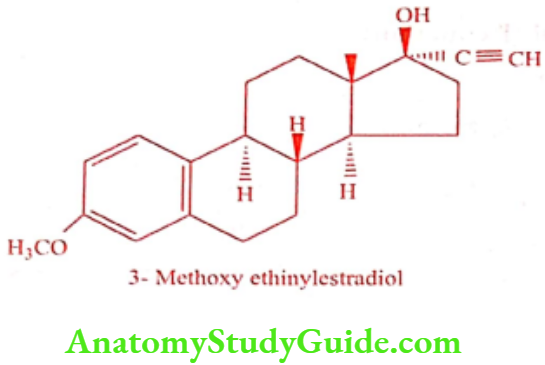
Mestranol is a semi-synthetic estrogen. Chemically it is 3-o-methyl ether of ethinylestradiol. It is a prodrug, following oral administration it metabolizes to Ethinylestradiol. It was incorporated with Norethynodrel and several progestins in oral contraceptives.
Synthesis
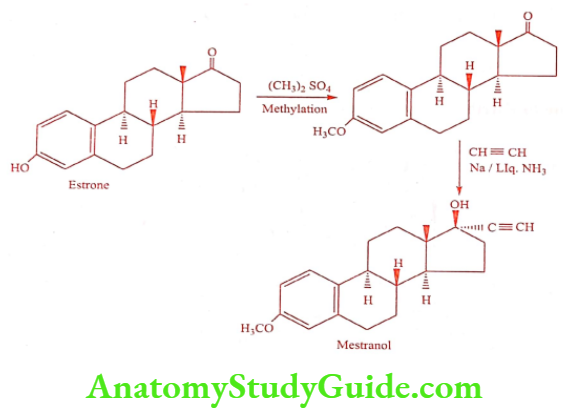
ADR: Pulmonary embolism, hypertension, endometrial carcinoma, and cerebral thrombosis.
Dose: 0.1 to 0.2mg/day/oral.
Use: It is an effective estrogen, used in combination with Progesterone. It is not marketed as a single entity.
Chemical Relationship among Estrone, Estriol and Estradiol
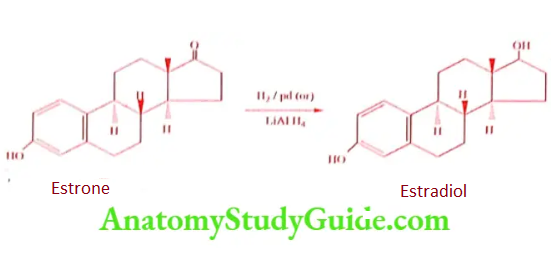
Estrone to Estradiol (Reduction)
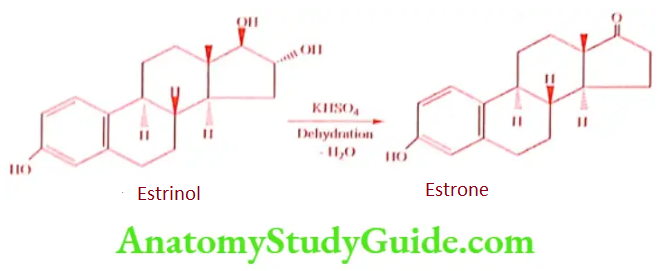
Estriol to Estrone (Dehydration)
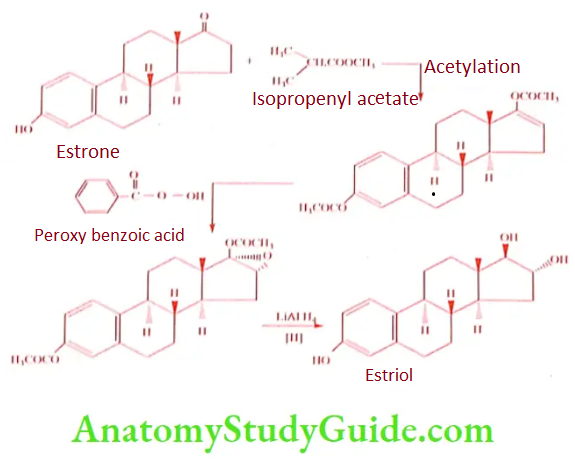
Estrone to Estriol
Non-Steroidal Estrogen
As a result of numerous studies and extensive knowledge regarding the SAR of estrogen, it is found that the steroidal nucleus is not required for estrogenic activity. The aromatic ring A and hydroxy group at position 3 are essential for activity.
- The distance between C3 and C17 oxygen atom should range from 10.3 to 12.1 A° for optimum activity. Substitution in the 1st position and additional hydroxylation at 6th, 7th, and 11th positions reduces the activity.
- Substitution of methoxy, ethyl group at 11ẞ position increases activity.
- The removal of 3rd or 17th hydroxyl group or epimerization of the 17ẞ-hydroxy group to a-configuration results in the less active compound.
- The presence of the ethinyl or vinyl group in the 17th position increases the activity whereas the polar group in that position reduces the activity. Enlargement of the rind reduces the activity.
Diethylstilboestrol (Stilboestrol)
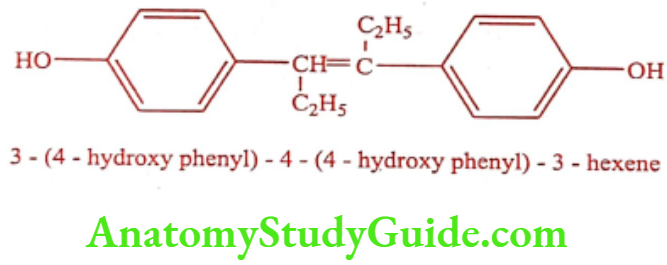
Stilboestrol exists in cis and trans form. Trans Stilboestrol is 10 fold more potent estrogenic than its cis isomer. It is more active than oestrogen when administered subcutaneously. It can also be given orally.
Stilboestrol have similar activity as that of Estradiol or other natural estrogens when compare the structure of Stilboestrol with natural estrogens, estradiol with ring B and C open and a 6 carbon ring D. The distance between the two Stilboestrol phenolic- OH groups was the same as that of C3-OH or C17-OH distance of estradiol. Therefore, they could both fit the same receptor. The OH to OH distance in Stilboestrol is 12.1A°, where as 10.9A° in estradiol.
Synthesis
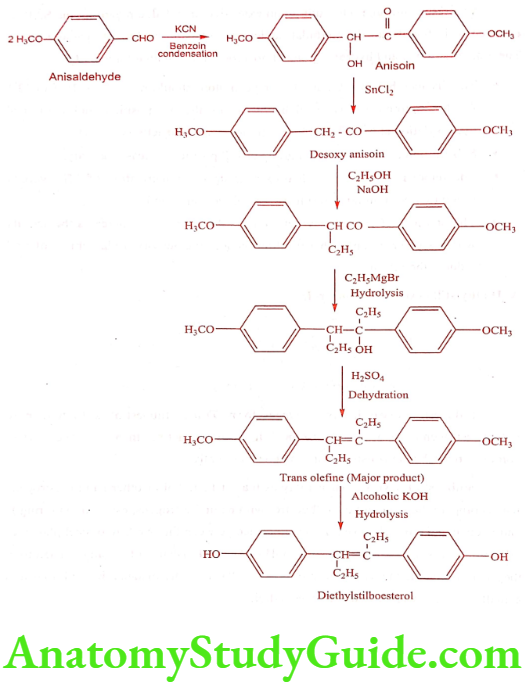
ADR: GI disturbances, jaundice, hypercalcaemia and loss of diabetic control.
Dose: 10 to 20mg daily.
Use: Palliative treatment of malignant breast neoplasm in post menopausal.
Gestogens (Corpus Luteum Hormones)
The natural gestogen is Progesterone, which is secreted mainly by the corpus luteum portion of the ovary. Small amounts are also secreted by the testes in the male and the adrenal cortex in both sexes and large amounts are secreted by the placenta.
Example: Progesterone.
Classification
- Natural progestins:
- Example: Progesterone, Hydroxyprogesterone, Medroxyprogesterone, Megestrol.
- Synthetic progestins:
- Testosterone derivatives :
- Example: Ethisterone, Dimethisterone,
- 19 Nortestosterone derivatives:
- Example: Norethindrone, Norethynodrel, Ethynodiol, Norgestrel, Norgestimate, Norelgestromin, Desogestrel, Etonogestrel.
- Testosterone derivatives :
- Miscellaneous synthetic progestins:
- Example: Trimegestone, Drospirenone.
Natural Progestins
Progesterone (Progest, Proluton)
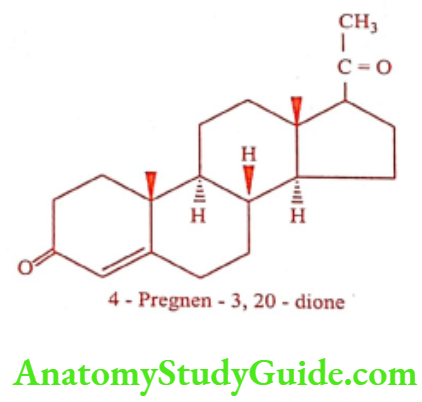
Progesterone is the main hormone of the corpus luteum and placenta. Progestogens are necessary for certain changes which occur in the uterus and vagina during menstrual cycle, for the development of mammary tissue and for the maintenance of pregnancy. It is not active orally.
Progesterone is produced in the ovary and adrenal glands and during pregnancy in the placenta. It is stored in adipose tissue. In mammals, it is bio-synthesized from pregnenolone which is derived from cholesterol. Progesterone is a precursor of mineralocorticoids Aldosterone, Testosterone, Estrone and Estradiol.
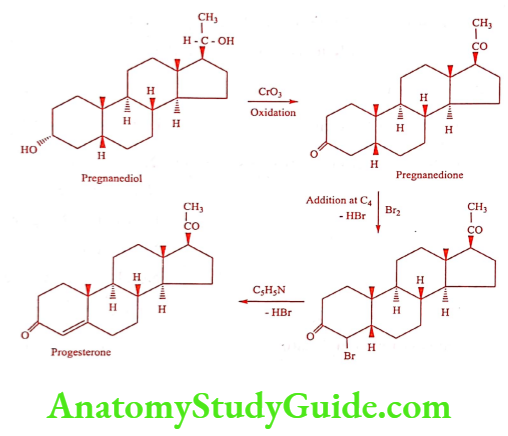
Synthesis
Method 1: Synthesis of Progesterone from Pregnanediol
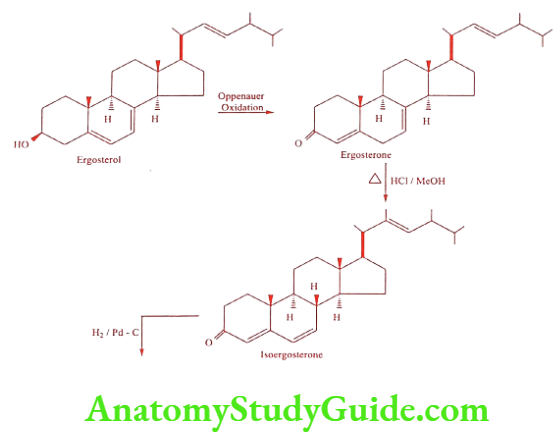
Method 2: Synthesis of Progesterone from Ergosterol
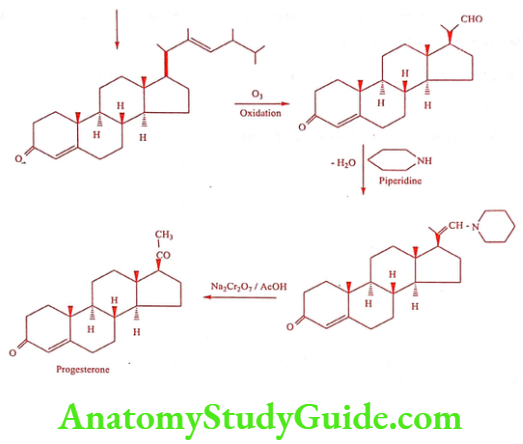
ADR: Head ache, edema, acne and mood swing.
Dose: 100 to 400mg orally once daily.
Use: Progesterone and other progestogens are used in the treatment of functional uterine bleeding. It is given along with estrogen in menstrual disorder and also given in the treatment of neoplasm of the breast and the endometrium.
Hydroxyprogesterone (Proluton Depot, Procaprin)
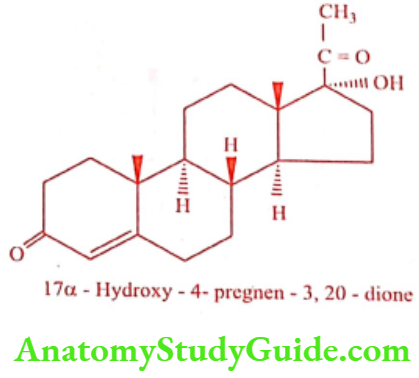
ADR: Head ache, edema, acne, mood swing and irregular bleeding.
Dose: 250 to 500mg i.m at 2 to 14 days intervals. Progesterone is light sensitive and should be protected from light.
Use: It is useful in the palliative treatment of advanced endometrial breast and renal carcinoma.
Medroxyprogesterone (Farlutal, Provera)
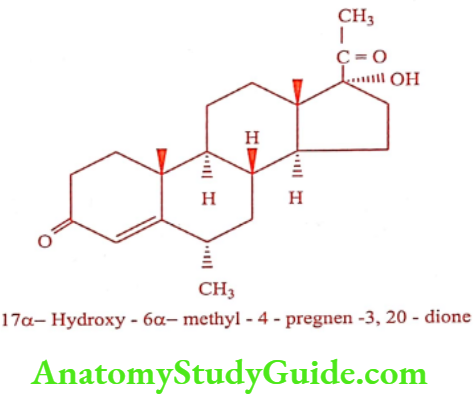
ADR: Head ache, edema, acne and mood swing.
Dose: 5 to 20mg/day.
Use: It is useful in the treatment of endometrial, breast and renal carcinoma. It plays an important role in birth control products.
Synthetic Progestins
19-Nortestosterone derivative
Norethindrone (Norgest, Regestrone)
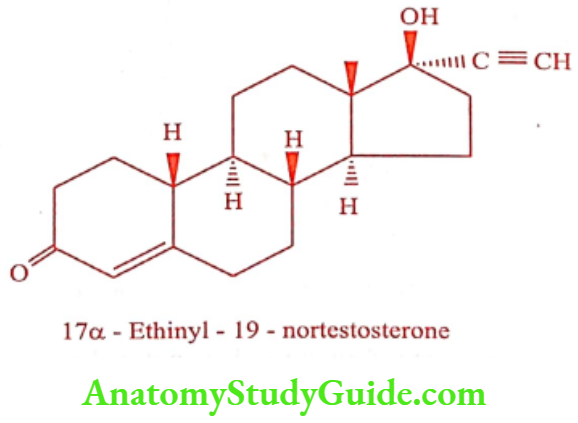
ADR: Head ache, edema, acne and mood swing.
Dose: 5 to 10mg/ day at bet time.
Use: It is orally active and more potent drug than Progesterone. It is used as oral contraceptive tablets or pills.
Megestrol (Megace)
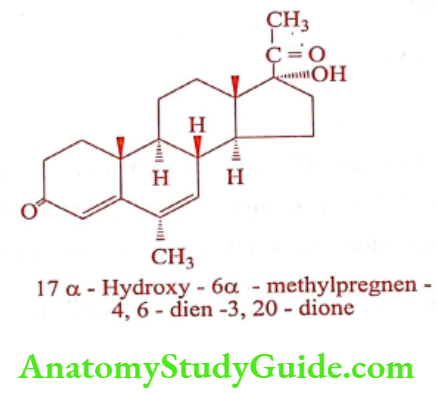
ADR: Decreased sexual desire, unexpected vaginal bleeding, difficulty in sleep, dizziness, and weakness.
Dose: 800mg/day.
Use: It is used in the treatment of breast and endometrial carcinoma and in post- menopausal women with advanced hormone-dependent carcinoma.
Adrenocorticoids
The Adrenal gland, located below kidney is a flat and cap like structure. The cortex (shell) of the gland synthesizes steroid hormones known as adrenocorticoids, whereas the medulla (inner core) of the gland secrets catecholamines. The adrenocorticoids include glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids.
Glucocorticoids regulate carbohydrates, proteins and lipid metabolism. Mineralocorticoid regulates salt balance and water retention. The decreased secretion of steroidal hormone by the adrenal cortex results in Addison’s disease (named after Thomas Addison) characterized by weakness, anorexia, hypotension, vomiting, hyperpigmentation of the skin, and mental depression.
Cushing syndrome is hyperadrenalism, increased secretion of adrenocorticotropin hormone due to pituitary carcinoma. The inability of the adrenal cortex to carry 17-a hydroxylation from cholesterol during the biosynthesis of the hormone, results in increased aldosterone level, characterized by polyurea, alkalosis, hypernatremia, and hypertension is known as Conn’s syndrome.
The most important hormonal steroids produced by the adrenal cortex are aldosterone primary mineralocorticoids in humans and hydrocortisone primary glucocorticoids in humans. Adrenal cortex hormones are classified into two classes.
- Glucocorticoids
- Mineralocorticoids
Glococorticoids
Glucocorticoids are secreted by the adrenal cortex, which affect carbohydrate and protein metabolism, and which favor lipolysis called glucocorticoids. They exert a regulatory influence on lymphocytes, erythrocytes and eosinophils of the blood.
Use: Glucocorticoids are used in the treatment of collagen vascular diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, disseminated lupus erythematous, and dermatomyositis. They are also used topically, orally and parenterally in the treatment of anti-inflammatory conditions. They also provide relief from symptoms of allergies like hay fever, dermatitis, eczema, etc.
Classification
- Glucocorticoids with moderate to low salt retention properties
- Natural Glucocorticoids :
- Example: Cortisone, Hydrocortisone
- Synthetic Glucocorticoids :
- Example: Prednisone, Prednisolone.
- Natural Glucocorticoids :
- Glucocorticoids with ion salt retention properties:
- Example: Methylprednisolone, Betamethasone, Dexamethasone, Amcinolone, Flucinolone, Triamcinalone, Paramethasone, and Flumethasone.
- Ophthalmic glucocorticoids :
- Example: Medrysone, Fluorometholone, Rimexolone.
- Glucocorticoids for asthma and allergic rhinitis:
- Example: Triamcinolone, Beclomethasone, Flunisolide, Budesonide, Mometasone, Fluticasone, Ciclesonide, Hydrocortisone, Methylprednisolone, Prednisolone.
Natural Glucocorticoids
Cortisone (Corlin)
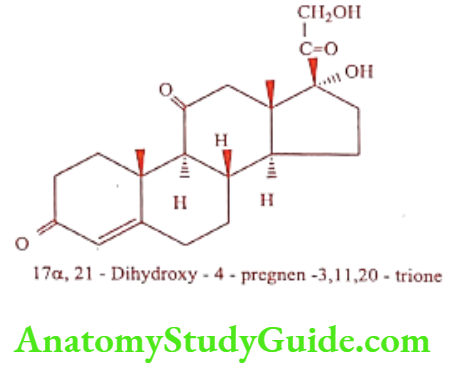
Cortisone is naturally occurring cortisone, with good systemic anti-inflammatory activity and low-to-moderate salt retention activity. It is official as Cortisone acetate
ADR: Sodium and fluid retention, muscle wasting and osteoporosis.
Dose: 20 to 100 mg/day orally.
Use: It is used in the treatment of collagen diseases, Addison’s disease, severe shock, allergic conditions and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Hydrocortisone (Cort-S, Multicort)
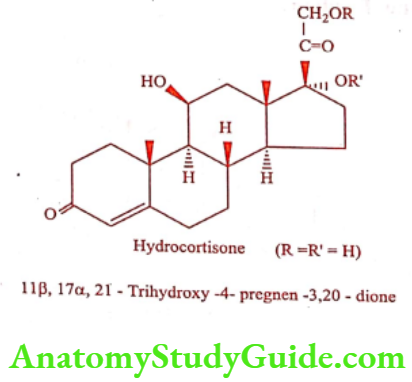
Hydrocortisone is the primary natural glucocorticoid in humans. It contains – OH group C11, instead of keto group, when compared the structure of Cortisone. The commercially available salts and esters are given in Table.
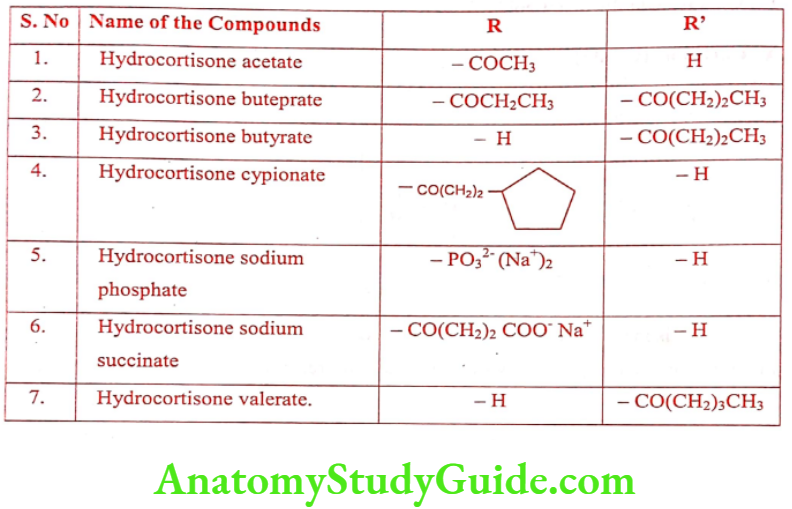
ADR: Sodium and fluid retention, potassium and calcium depletion, and osteoporosis.
Dose: 20 to 30mg daily in two divided doses.
Use: It is mainly used in replacement therapy, shock, status asthmatics, and acute adrenal insufficiency.
Synthetic Glucocorticoids
Prednisolone (Predone, Predcip)
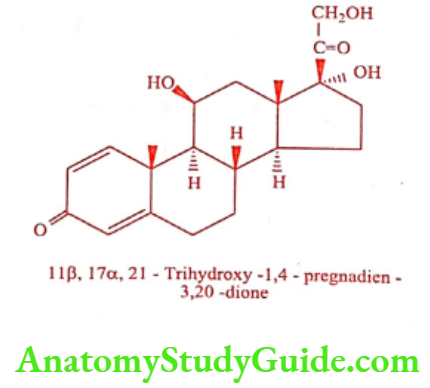
Prednisolone is A’hydrocortosone. It is a corticosteroid drug with predominant glucocorticoid and low mineralocorticoid activity.
ADR: Cushing’s syndrome, growth retardation in children, osteoporosis, and peptic ulceration.
Dose: 2.5 to 60mg daily, as a single daily dose or as a double dose on alternative dates in two divided doses.
Use: It is used for allergic, inflammatory, autoimmune diseases and in malignancies
Prednisone (Deltasone, Winpred)
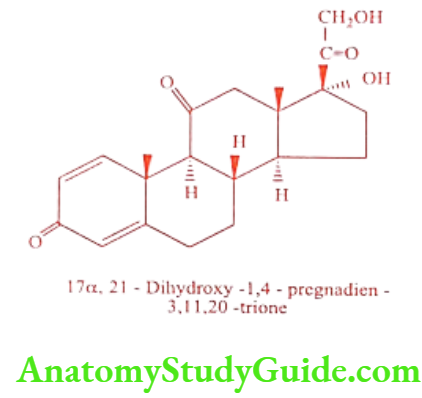
Prednisone is ‘cortisone. Activity is similar to Prednisolone because of low salt retention activity it is preferred over cortisone and hydrocortisone. It is a prodrug, in the liver it is converted in to Prednisolone by 11-ẞ-Hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase.
ADR: Euphoria, insomnia, headache, hypertension, edema, nausea, and vomiting.
Dose: 5 to 60mg daily in single dose or divided doses. Maximum daily dose is 250mg.
Use: It is used in the treatment of acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis, pulmonary or extrapulmonary tuberculosis, certain inflammation, certain types of cancer and as a drug regimen to prevent rejection of post-organ transplant.
Methylprednisolone (Mypred, Premisol)
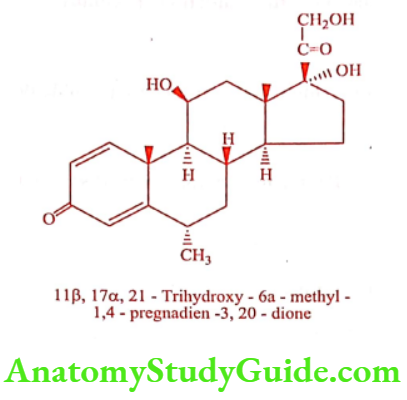
An additional double bond between C1 and C2 in Cortisone and Hydrocortisone constitutes the structure of Prednisone and Prednisolone respectively. Prednisone has 3 to 5 times the glucocorticoid activity of Hydrocortisone, but somewhat less mineralocorticoid activity. Prednisone in pediatrics is widely used to treat nephrosis, rheumatic carditis, leukemia’s, other tumors and tuberculosis.
Prednisolone is 4 times as potent as Hydrocortisone, for glucocorticoids, but it is a weaker mineralocorticoid. It is available as acetate, sodium phosphate and tebutate salt.
Methylprednisolone possess a weak mineralocorticoid activity, it is not employed in the management of acute adrenal insufficiency. It is also available as acetate and sodium succinate salt.
ADR: Hypertension, edema, arrhythmia, and GI disturbances.
Dose: Initially, 2 to 60mg/day in 1 to 4 divided doses, followed by a gradual reduction in dosage to the lowest possible level consistent with maintaining an adequate clinical response.
Use: It is used for allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases and as a retention edema in ulcerative colitis. It is mainly used in replacement therapy, shock, status asthmatics, and acute adrenal insufficiency.
Fluoro Derivatives
Betamethasone (Betnesol, Betnovate)
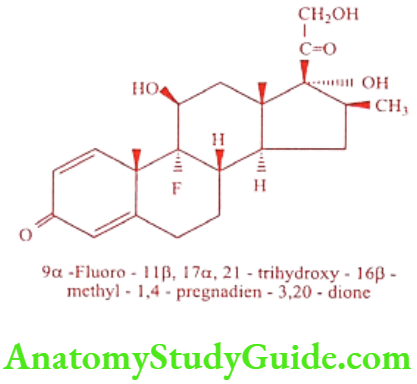
It has increased glucocorticoid and anti-inflammatory activities, but very low mineralocorticoid activity. It is effective with very low doses. It is available as variety of ester derivatives like Betamethason-17-valerate, Betamethason-21-acetate, Betamethason-21-sodium phosphate, Betamethason-17, 21-dipropionate. Unlike other drugs with these effects, it does not cause water retention.
ADR: Sodium and fluid retention, potassium and calcium depletion, and osteoporosis.
Dose: 0.5 to 5.0mg daily.
Use: It is used for inflammatory, and allergic conditions, also preferred in cerebral edema, skin irritation, and flake from eczema. The combination of Betamethasone dipropionate and salicylic acid is used to treat psoriasis.
Dexamethasone (Decdan, Decatron, Dexona)
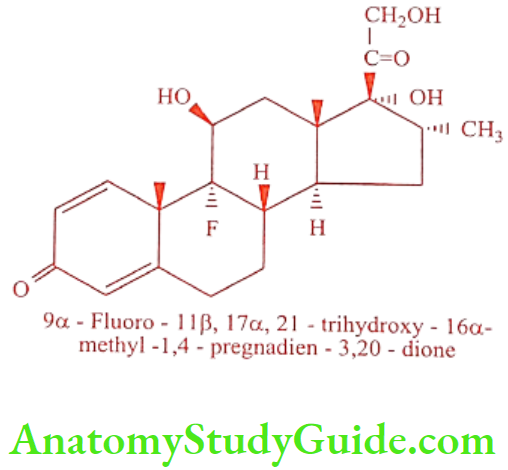
Dexamethasone is a 16a-isomer of Betamethasone. It is available as Dexamethasone-21- acetate, and Dexamethason-21-sodium phosphate. It possesses glucocorticoid activity. Its glucocorticoid potency is about 25 times as that of Cortisone.
ADR: Growth retardation, osteoporosis, peptic ulcer, glaucoma and subcapsular cataracts
Dose: 0.75 to 9mg daily in 2 to 4 divided doses.
Use: It is used for inflammatory, and allergic conditions and also preferred in cerebral edema and shock.
Triamcinolone (D-CORT, Tricort, Aristocort)
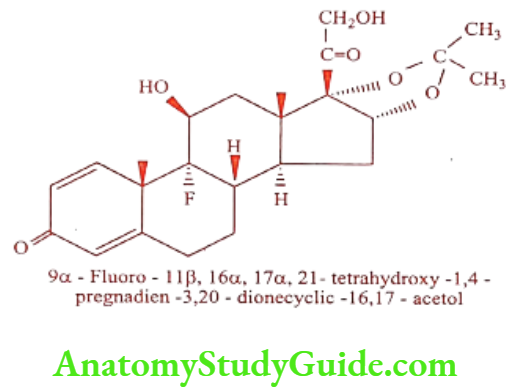
It is a long acting synthetic glucocorticoid, 7 to 13 times more potent than Hydrocortisone. It is available as acetonide, diacetate and hexacetonide salt.
ADR: Intracranial hypertension, Cushing’s syndrome and Growth retardation in children.
Dose: 4 to 12mg daily in single or divided doses.
Use: It is used for inflammation, allergic conditions, eczema, psoriasis, arthritis, ulcerative colitis, lupus, sympathetic ophthalmia, temporal arteritis and prevention of asthma attack. Triamcinolone acetonide is used as an endodontic lotion (tooth root canal).
Beclomethasone dipropionate(Becoride, Vanceril)
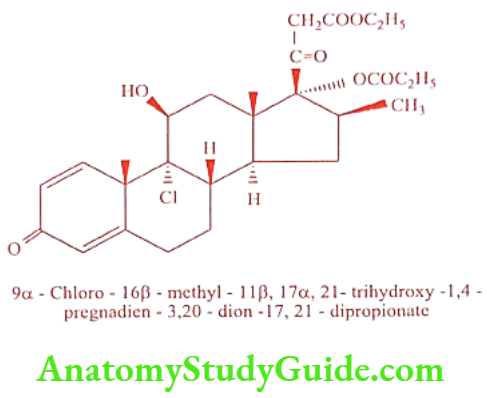
ADR: Headache, sinusitis and pain.
Dose: Initially 600 to 800μg daily followed by maintenance dose of 400μg daily in 2 to 4 divided doses.
Use: It is used as anti-inflammatory and asthmatic.
Structure Activity Relationship of Adrenocorticoids
Functional group essential for both mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids activity is
- Pregnane skeleton with all trans backbone.
- 17ẞ-Ketol side chain (Keto group at C20 & C21 hydroxyl group).
The C21 hydroxyl group must be free for both mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid activity.
The glucocorticoids are used for their anti-inflammatory effect and the skeletons have been synthesized with the intention of enhancing anti inflammatory activity and decreasing the salt retaining properties.
- An additional unsaturation in ring A enhances the anti-inflammatory and anti-rheumatic properties but reduces the sodium retention properties.
- Example: Prednisone has 4 times the anti-inflammatory activity of Cortisol and only 0.8 of mineralocorticoid activity.
- The presence of oxygen at position C11 is necessary for glucocorticoid activity but not for mineralocorticoid activity.
- The 11ẞ-hydroxy substitution is more potent than the 11- keto group
- The 11a-hydroxy group is also important for glucocorticoid activity.
- The 21-hydroxy group is essential for mineralocorticoid, but not for glucocorticoid activity.
- Introduction of either – CH3 or -OH groups at C16, reduces mineralocorticoid activity, but only slightly decreases glucocorticoid and anti-inflammatory activity.
- Example: Paramethasone (16a-methyl), Betamethasone (16ẞ-methyl), Dexamethasone (16a-methyl), Triamcinolone (16α-hydroxy) have no significant mineralocorticoid activity.
- 6α-methyl substitution enhances the mineralocorticoid activity of Cortisol.
- The 9α-fluoro group enhances both glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid activities.
Mineralocorticoids
Mineralocorticoids get their name from the effect on mineral metabolism. Steroids that secreted by adrenal cortex, which affect the electrolyte metabolism are called mineralocorticoids. It maintains the normal distribution of water and chloride ion and resulting in maintenance of blood volume and blood pressure.
The principle steroid with mineralocorticoid activity is Aldosterone. It acts on kidney to promote Na reabsorption and maintain normal blood pressure. Aldosterone also acts on sweat glands to reduce loss of Na* in perspiration and also on taste buds to increases the sensitivity of the taste buds to source of Na+
The relative or complete absence of adrenocortical function is called as Addison’s diseases, is accompanied by loss of sodium chloride and water, retention of K+, lowering of blood glucose and liver glycogen levels, increased sensitivity to insulin, nitrogen retention and lymphocytosis.
Deoxycorticosterone (Docabolin)
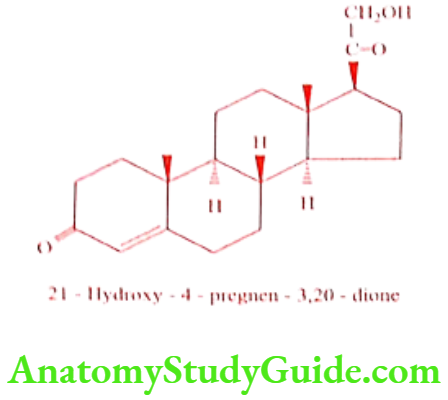
Synthesis
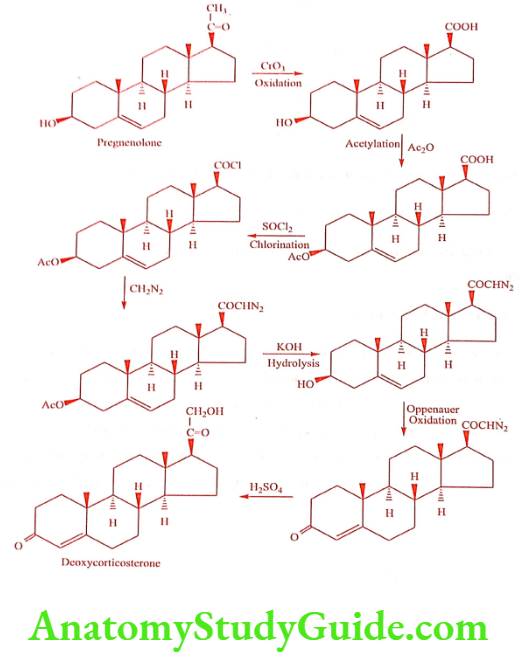
ADR: Sodium and water retention, edema and hypokalemic alkalosis.
Dose: 2 to 5mg sublingual once or twice weekly.
Use: It is used occasionally for replacement therapy in Addison’s diseases.
Fludrocortisone (Floricort)
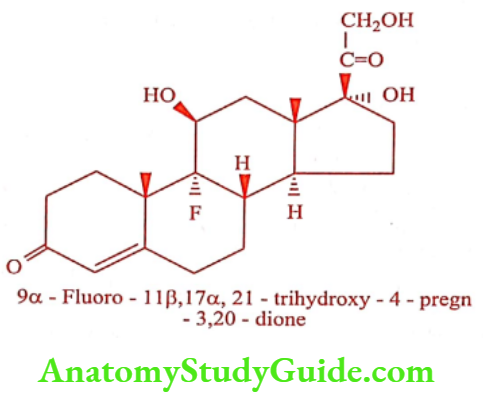
ADR: Sodium and water retention, edema and hypokalemic alkalosis.
Dose: 50 to 200μg daily.
Use: It is used for replacement therapy in Addison’s disease and congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Oral Contraceptives
Oral contraceptives are medicines taken by mouth to prevent pregnancy. They are also known as pills, OCs or birth control pills. They contain synthetic forms of two hormones produced naturally in the body. These hormones, estrogen and progestin, regulate the female menstrual cycle. Some types of oral contraceptives use only progestational hormones, but most use a combination of estrogen and progestin. Birth control pills do not completely protect a woman from getting sexually transmitted diseases.
Type of contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives fall into the following categories:
Steroidal contraceptives
- Combination pill
- Progestin only pill or mini pill
- Injectable depot hormonal contraceptives
- Trans dermal contraceptives
- Hormonal releasing implants, IUCDS, and vaginal rings
Non-steroidal contraceptives Example: Ormeloxifene.
Steroidal contraceptives
Combination Pill
It contains combination of estrogen and progestin. The Estrogen compound either Ethinylestradiol or Mestranol suppresses the Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) release. This prevents the formation of follicle during the follicular phase of menstrual cycle. The progestin component (many available) suppresses the luteinizing hormone (LH) and block ovulation. The combination tablet suppresses the production of FSH and/or LH and prevents ovulation.
This process is similar to the natural inhibition of ovulation during pregnancy. These agents can be either monophasic or multiphasic in their hormone composition. The monophasic combination of progestin and estrogen contains the same amount of drug in each active tablet. In the natural menstrual cycle, Progesterone plasma concentrations peak late in the cycle. The higher concentrations peak late in the cycle.
The higher Estrogen/Progesterone ratio early in the cycle develops endometrium. Endometrial effect that prevents implantation of the embryo in the uterus. The multiphasic formulation more closely mimics the natural changes in both hormone concentrations that occur throughout the menstrual cycle.
The variation in estrogen and progestin level in multiphasic combinations prevents the incident of spotting (break throughout bleeding) associated with monophasic combination. Adverse effects of oral contraceptive therapy include increased risk of stroke, acute myocardial infarction, thromboembolic cardio vascular disease, cervical cancer and weight gain.
Progestin only Pill or Mini Pill
The mini pill contains either Norethindrone or Norgestrel. The progestin only pill is given for those patients with contraindications to exogenous estrogen (e.g. smoking or high blood pressure), for old women in whom fertility is diminished or for lactating women who already experiencing prolactin-induced ovulation suppression. Adverse effect is limited because there is no estrogenic component.
Injectable Depot Hormonal Contraceptives (Depo-Provera)
Depo provera is a branded progesterone-only contraceptive, depot Medroxy progesterone acetate long acting reversible hormone contraceptive birth control drug.
ADR: Irregular bleeding and small weight gain.
Dose: Single dose 150 mg i.m. provides contraception for 3 months.
Transdermal Contraceptives
The product contains Norelgestromin and Ethinylestradiol. A patch is applied once a week for 3 weeks, followed by a week with no patch. 0.15mg Norelgestromin, and 0.02mg Ethinylestradiol is available in the brand name Ortho-Evra
Another contraceptive option is a flexible polymeric ring 2.1 inch in diameter that contains Etonogestrel and Ethinylestradiol (Nuvaring). The ring is inserted inside the vagina for 3 weeks.
Hormone-Releasing Implants, IUCDS and Vaginal Ring
The Progestasert IUD has microcrystalline progesterone dispersed in silicone oil. The dispersion is contained in a flexible polymer in the shape of T. The polymer acts as a membrane to permit 65 mg of progesterone to be released slowly into the uterus each day for 1 year.
Levonorgestrel-releasing IUD is another interuterine device containing 52mg of Levonorgestrel. An intrauterine ring is another contraceptive option. A new ring is inserted 1 week after the removal of the prior ring. The ring contains 11.7mg of Etonogestrel and 2.7mg of Ethinylestradiol. Six flexible silastic (Dimethyl siloxane / Norgestrel copolymer) Capsules containing Levonorgestrel available in the trade name Norplant is an implanted contraceptive. The capsule is implanted in the mid portion of the upper aim and provides conception for 5 years.
Non-steroidal contraceptives
Ormeloxifene (Centron, Dovex-DS, Saheli, Sevista)
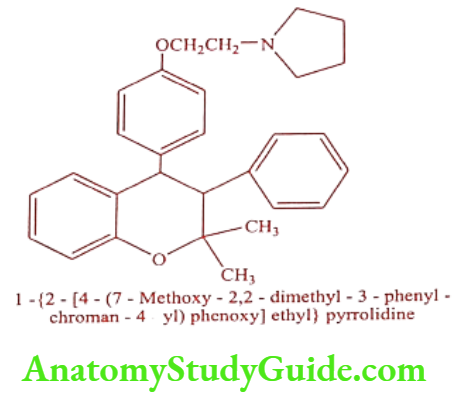
Mechanism of Action: Ormeloxifene is a selective estrogenic receptor modulator. In some of the body, its action is estrogenic (e.g. bones) and in other parts of the body it’s antiestrogenic
Example: Uterus, breast
It causes an asynchrony in the menstrual cycle between ovulation and the development of the uterine lining, so that fertilization occurs, but implantation will not be possible.
ADR: Urinary incontinence.
Dose: 30mg weekly.
Use: It is used as a contraceptive, for dysfunctional uterine bleeding and breast cancer.
Leave a Reply