Partial Coverage Restorations Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. What are the advantages of using full crown restorations over partial veneer restorations?
Table of Contents
- Preserving tooth structure.
- Easy cleaning of margins by patient.
- Providing better retention.
- Less periodontal irritation.
- Less pulpal problems.
Note: Providing better resistance form also.
Answer. 3. Providing better retention.
Read And Learn More: Fixed Partial Denture Short Essay Question And Answers
Question 2. The proximal half crown.
- Is indicated in a 60 degree rotated tooth.
- Has the facial surface of the tooth left intact.
- Is indicated in patients with good oral hygiene.
- Is indicated in severely lingually inclined teeth.
- Is indicated in a defective distal surface.
Answer. 3. Is indicated in patients with good oral hygiene.
Question 3. The mandibular reverse three-quarter crown.
- Is indicated in severe labially inclined teeth.
- Is indicated in 90 degree rotated teeth.
- Tooth preparation includes an occlusal shoulder.
- Has grooves that are placed at linguoproximal line angles.
- Tooth preparation is extended to the non-functional cusps.
Answer. 4. Has grooves that are placed at linguoproximal line angles.
Question 4. The seven-eighths crown.
- Is indicated in a severely labially inclined tooth.
- Is indicated in a 90 degree rotated tooth.
- Is indicated in a tooth which needs the distofacial cusp to be covered.
- Tooth preparation includes an occlusal shoulder.
- Tooth preparation has poor resistance and retention form.
Answer. 3. Is indicated in a tooth which needs the distofacial cusp to be covered.
Question 5. The most common cause of failure in resin bonded bridge is:
- Inadequate taper.
- Loss of retention.
- Failure of connector.
- Perforation.
- Occlusal wear.
Answer. 2. Loss of retention.
Question 6. Which one of the following indirect restoration is less invasive?
- Full metal crown.
- Porcelain-fused-to-metal crown.
- Resin-bonded bridge.
- Full porcelain crown.
- Three quarter metal crown.
Answer. 3. Resin-bonded bridge.
Question 7. A resin-bonded bridge is best suited to replace a:
- Missing mandibular incisor.
- Missing mandibular canine.
- Missing mandibular 1st and 2nd premolar.
- Missing maxillary canine.
- Missing maxillary 1st and 2nd premolar.
Answer. 1. Missing mandibular incisor.
Question 8. The type of finish line for a resin-bonded bridge is:
- Knife edge.
- Shoulder.
- Radial shoulder.
- Chamfer.
- Deep chamfer.
Answer. 4. Chamfer.
Question 9. The placement of proximal groove will be on the ______ for a resin-bonded bridge:
- Facioproximal line angle.
- Lingual proximal line angle.
- Mesioproximal line angle.
- Distoproximal line angle.
- Faciolingual line angle.
Answer. 1. Facioproximal line angle.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1. In the following picture, four different forms of proximal groove on 3/4 crown preparation are shown. Identify which groove preparation is correct and why?
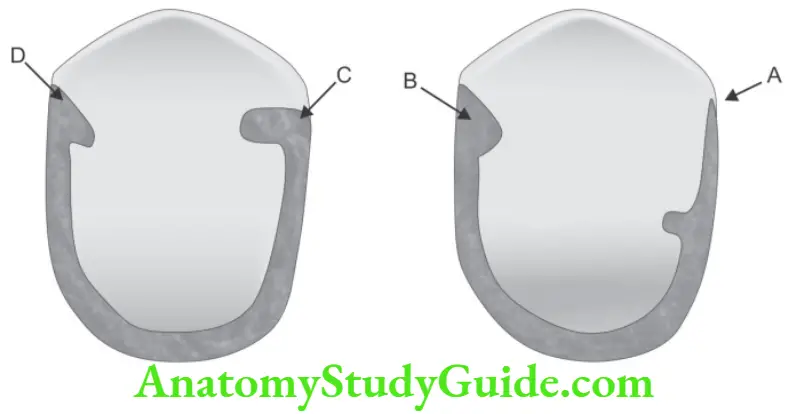
D is correct
Because of definite lingual wall which resist displacement.
Question 2. From the following picture answer the questions.
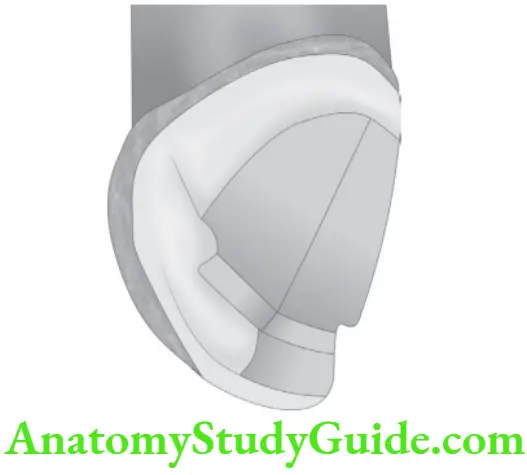
What is this type of preparation on upper canine called?
Three quarter restoration.
How should the axial surface and proximal grooves be related to the facial surface to improve retention and resistance form?
To improve on retention the axial surface and proximal grooves should be parallel to Incisal one-half to two thirds of the facial surface of the tooth.
What will happen if proximal grooves incline labially?
Retention and resistance is compromised.
What is the depth of lingual reduction? And what is the suitable bur to prepare this?
0.7 mm, small wheel diamond.
Fill in the blanks
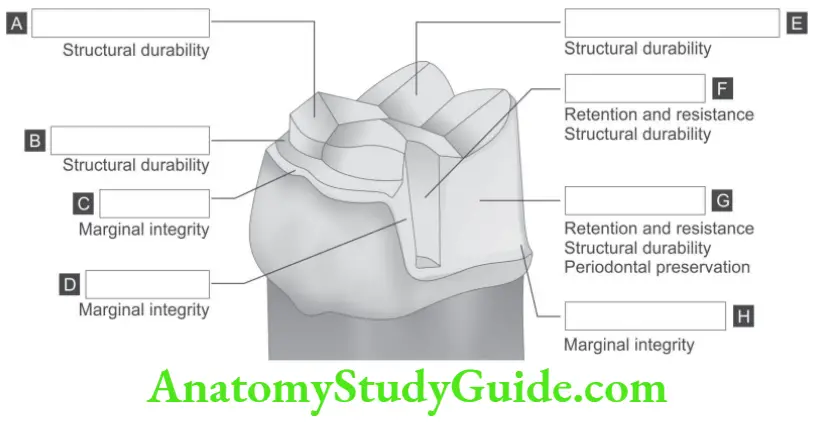
Question 1. On the following schematic picture of maxillary three-quarter crown preparation on premolar teeth state the function or name of each feature where indicated.
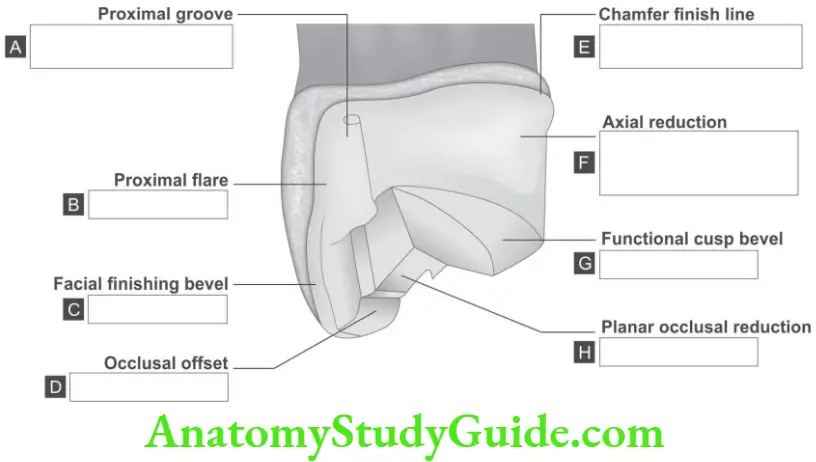
Answer.
A. Retention and resistance, structural durability
B. Marginal integrity
C. Marginal integrity
D. Structural durability
E. Marginal integrity. Periodontal preservation
F. Retention and resistance, structural durability, periodontal preservation
G. Structural durability
H. Structural durability
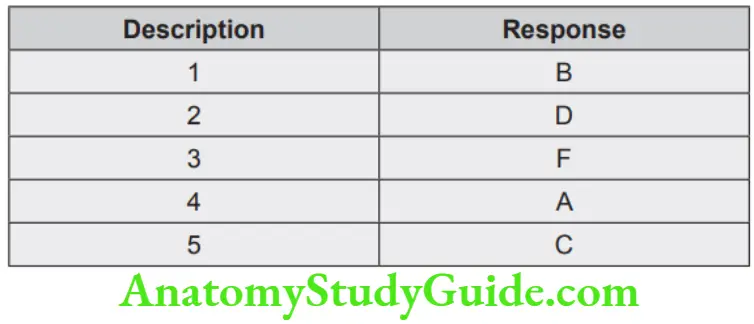
Question 2. On the following schematic picture of maxillary three-quarter crown preparation on canine teeth state the function or name of each feature where indicated.
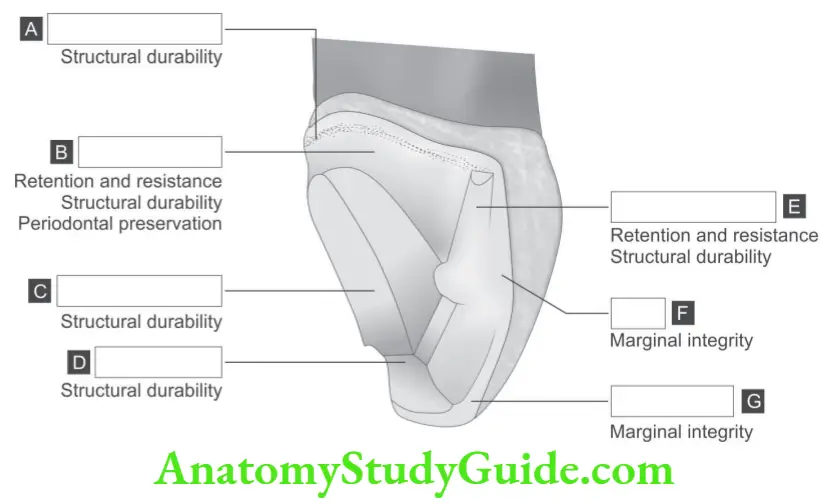
Answer.
A. Chamfer finish line
B. Axial reduction
C. Lingual reduction
D. Incisal offset
E. Incisal bevel
F. Flare
G. Incisal bevel
Question 3. On the following schematic picture of mandibular three-quarter crown preparation on molar teeth state the function or name of each feature were indicated.
Answer.
A. Function cusp bevel
B. Occlusal shoulder
C. Facial bevel
D. Proximal flare
E. Planar occlusal reduction
F. Proximal groove
G. Axial reduction
H. Chamfer finish line
Intracoronal restorations
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which one of the following statements about the porcelain inlay restoration is correct:
- It has poor esthetics.
- It is highly wear-resistant.
- It creates postoperative sensitivity.
- It undergoes polymerization shrinkage.
- It does not require cementation.
Answer. 2. It is highly wear-resistant.
Question 2. Which one of the following statements is correct about an indirect onlay restorations:
- It is indicated in root canal treated teeth with intact buccal and lingual cusps.
- The onlay preparation is more conservative than an inlay preparation.
- It is used as a retainer for long-span bridges.
- The retention mechanism is a “sleeve”.
- Internal buccal and lingual walls should be convergent.
Note: It is also indicated in a mesio-occluso-distal cavity with wide isthmus.
Answer. 1. It is indicated in root canal treated teeth with intact buccal and lingual cusps.
Question 3. Which following statements are correct about inlay preparation:
- The width of Isthmus should be buccolingually about 1/2 of B-L width.
- Occlusal contact should be included in the outline.
- Bevel on gingival margins should be narrower and more acute than occlusal margins.
- Onlay restoration is recommended over MOD inlay on premolar.
Answer. 4. Onlay restoration is recommended over MOD inlay on premolar.
Extended Matching Questions
Question 1. Theme : Tooth preparation

The above diagram illustrates preparation for a posterior metal only. Match the name of the features with their function and location on the diagram.
- Gingival bevel.
- Lingual flare.
- Isthmus.
- Occlusal shoulder.
- Proximal box.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1. Name the type of retention provided by indirect metal inlay restorations.
Wedge retention.
Question 2. What is the role of dove tail in class II metal inlay preparation? And how much is its depth?
Horizontal retention and resistance to avoid horizontal dislodgment of the restoration, 1.5 mm.
Question 3. How much is the maximum width of isthmus?
About ¼ of buccolingual width of the tooth.
Question 4. In class 2 metal inlay what preparations should be carried out on the buccal, lingual and gingival margins?
Flare on buccal and lingual walls.
Bevel on gingival wall (30–45˚).
Fill in the blanks
Question 1. In onlay preparation the function of occlusal shoulder is to provide________________.
Answer. structural durability
Question 2. In onlay preparation the function of proximal box is to provide ________________________.
Answer. retention and resistance, structural durability
Question 3. In onlay preparation the function of isthmus is to provide __________________________.
Answer. retention and resistance, structural durability
Provisional Restoration Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The percentage of shrinkage undergone by poly (methyl methacrylate) when it polymerizes is:
- 8%.
- 12%.
- 15%.
- 20%.
- 2%.
Answer. 1. 8%.
Question 2. What type of provisional restoration is given for the patient after a small intracoronal inlay preparation?
- Zinc oxide eugenol cement.
- Zinc phosphate cement.
- Calcium hydroxide cement.
- Glass ionomer cement.
- Composite restoration.
Answer. 1. Zinc oxide eugenol cement.
Question 3. One of the advantages of the direct technique of making a provisional restoration is:
- Protection of the pulp.
- Reduction in polymerization shrinkage.
- Reduction in laboratory time.
- Providing a better marginal fit.
- Providing better esthetics.
Answer. 3. Reduction in laboratory time.
Question 4. The external surface form in a provisional restoration:
- Can be customized.
- Only preformed.
- Replicates the prepared tooth surface.
- Replicates the edentulous ridge.
Answer. 1. Can be customized.
Extended Matching Questions
Question 1. Theme: Provisional restoration
A. Aluminium shell crown.
B. Cellulose acetate crown.
C. Preformed base-metal crown.
D. Cast metal restoration.
E. Polymethyl methacrylate crown.
F. Polycarbonate crown.
G. Polyvinyl ethyl methacrylate crown.
Using a letter from A to G, choose the most appropriate material from the list above that best matches each of the following descriptions numbered 1–5 below. You may use each option once only or not at all.
Customized provisional crown with poor color stability.
Customized provisional crown used as treatment restorations.
Preformed clear shell used to make direct provisional crowns.
Provisional preformed crowns used for posteriors in case of trauma.
Provisional crown which has significant presence of free monomer.

Question 2. Theme: Provisional restoration
A. Alginate.
B. Zinc oxide eugenol.
C. Impression compound.
D. Polymethyl methacrylate.
E. Polycarbonate.
F. Type 1 plaster.
G. Type 2 plaster.
Using a letter from A to G, choose the most appropriate material from the list above that best matches each of the following descriptions numbered 1–5 below. You may use each option once only or not at all.
An impression material used to make dentate working models.
Material used to make indirect provisional crown.
Preformed shell used to make direct provisional crowns.
Material used to cement the provisional crown.
Material used to make the diagnostic models.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1. 1. List two reasons as to why an indirect technique of fabricating a provisional restoration is preferred over a direct technique.
- Accuracy
- Avoid locking in undercuts
- Protection to pulp
- Improved fit or reduction in shrinkage
- Improved marginal fit
- Less clinical time [or more lab work].
2. List any four requirements for a provisional restoration.
- Pulpal protection
- Protects the remaining tooth structure
- Positional stability
- Occlusal function
- Easily cleaned
- Nonimpinging margins
- Strength and retention
- Esthetics.
3. Name two different types of resin materials that can be used for fabricating custom provisional restorations.
- Poly (methyl methacrylate)
- Poly (ethyl methacrylate)
- Poly (vinyl ethyl methacrylate)
- Bis-acryl composite resin
- Visible light-cured (VLC) urethane dimethacrylate
- Epimine resin.
Question 2. List the three techniques for fabricating an interim restoration.
- Indirect technique
- Direct technique
- Indirect–direct technique.
Question 3. Name the techniques for making a mold to form the outer surface of a custom provisional restoration that provides the appearance of a tooth where needed.
- Overimpression
- Template
- Shell crown.
Question 4. When you think an overimpression is not possible to make intraorally? What is the procedure of making an overimpression in that case?
Tooth with any defects – diagnostic cast – filled with utility wax – overimpression.
Fill in the blanks
Question 1. Placing the poly (methyl methacryylate) provisional restoration in a pressure pot under 20 Psi for polymerization decreases ___________ and increases the ___________ .
Answer. porosity, transverse strength
Question 2. The indirect technique of making a provisional restoration is preferred over the direct technique for its ___________.
Answer. accuracy
Question 3. ___________ is used to remove the excess cement from the interproximal region after crown cementation.
Answer. dental floss
Fluid control Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which is the best fluid control technique when the lone dentist does a filling in the 14?
- Saliva ejector.
- Svedopter.
- Rubber dam.
- High-volume vaccum.
Answer. 1. Saliva ejector
Question 2. Which is the best fluid control technique when the lone dentist does a filling in the 41?
- Saliva ejector.
- Svedopter.
- Rubber dam.
- High-volume vaccum.
Answer. 2. Svedopter
Question 3. Which is the best fluid control technique when the dentist does an elastomeric impression of the maxillary arch?
- Saliva ejector.
- Svedopter.
- Rubber dam.
- High-volume vaccum.
Answer. 1. Saliva ejector
Question 4. Which is the best fluid control technique when the dentist does an elastomeric impression of the mandibular arch?
- Saliva ejector.
- Svedopter.
- Rubber dam.
- High-volume vaccum.
Answer. 2. Svedopter
Question 5. The most appropriate fluid control aid when taking an elastomeric impression of the maxillary arch is:
- A saliva ejector.
- Cotton rolls.
- A tongue deflector.
- High-volume evacuator.
- Anti-sialagogues.
Answer. 1. A saliva ejector.
Question 6. Name the antisialagogue which is an antihypertensive agent.
- Banthine.
- Propantheline bromide.
- Clonidine hydrochloride.
Answer. 3. Clonidine hydrochloride.
Question 7. To prevent lateral penetration of heat into the tissues with subsequent injury, the electrode should move at a speed of no less than __________ and if it is necessary to retrace the path of a previous cut, __________ should be allowed to elapse before repeating the stroke.
- 7 mm per second/8–10 seconds.
- 17 mm per second/18–20 seconds.
- 20 mm per second/28–30 seconds.
- 30 mm per second/38–40 seconds.
Answer. 1. 7 mm per second/8-10 seconds.
Question 8. The most appropriate method for removing a limited amount of epithelial tissue to expose and record the finish line after crown preparation is:
- Electrosurgery.
- Rubber dam.
- Antisialagogues.
- Cotton rolls.
- Rotary curettage.
Answer. 5. Rotary curettage.
Question 9. The most appropriate method for removing inflamed tissue that has proliferated over the crown margin line is:
- Electrosurgery.
- Rubber dam.
- Antisialagogues.
- Copper band.
- Rotary curettage.
Answer. 1. Electrosurgery.
Question 10. Most effective isolation aid in fluid control [displaces gingiva by compression only].
- Electrosurgery.
- Rubber dam.
- Antisialagogues.
- Cotton rolls.
- Rotary curettage.
Answer. 2. Rubber dam.
Question 11. Effectively carries the impression material and displaces the gingiva.
- Electrosurgery.
- Rubber dam.
- Antisialagogues.
- Copper bands.
- Rotary curettage.
Answer. 4. Copper bands.
Question 12. Which one of the following achieves gingival displacement by combining chemical and mechanical methods?
- Electrosurgery.
- Rubber dam.
- Retraction cords.
- Copper bands.
- Rotary curettage.
Answer. 3. Retraction cords.
Question 13. The purpose of retracting the gingiva before making an impression is:
- Improving the esthetics of final restoration.
- Exposing the finish line only.
- Recording the unprepared tooth surface below the finish line.
- Recording the gingival margin below the finish line.
- Protecting the soft tissue only.
Answer. 3. Recording the unprepared tooth surface below the finish line.
Extended Matching Questions
Question 1. Theme: Fluid control and soft tissue management
A. Electrosurgery.
B. Copper bands.
C. Retraction cord.
D. Rubber dam.
E. Antisialagogues.
F. Cotton rolls.
G. Rotary curettage.
Using a letter from A to G, choose the most appropriate fluid control and soft tissue management aid from the list above that best matches each of the following descriptions numbered 1–5 below. You may use each option once only or not at all.
- Limited removal of epithelial tissue in the sulcus to expose the finish line.
- Removal of irritated proliferated tissue over the finish line.
- Displaces gingiva only by compression.
- Effectively carries the impression material and displaces the gingiva.
- Displaces gingiva by combining chemical and pressure packing.

Short Answer Questions
Question 1. With regards to the gingival tissue management following tooth preparation:
1. List three mechanical means of finish line exposure before taking the final impression.
- Copper band
- Rubber dam
- Plain cotton cord.
2. List three antisialagogues used in fluid control.
- Methantheline bromide (Banthine)
- Propantheline bromide (Pro-Banthine)
- Clonidine hydrochloride.
Note: Action – Gastrointestinal anticholinergics that act on the smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal, urinary and biliary tracts producing dry mouth as side effect.
3. What are the four signs of “epinephrine syndrome”?
- Tachycardia
- Rapid respiration
- Elevated blood pressure
- Anxiety, and postoperative depression.
Question 2. In relation to the gingival tissue management after tooth preparation
1. What are the three factors which determine the suitability of gingiva for the use of rotary curettage?
- Absence of bleeding upon probing
- Sulcus depth less than 3.0 mm
- Presence of adequate keratinized gingival.
2. Name the four forms of currents used in electrosurgery and its tissue response.
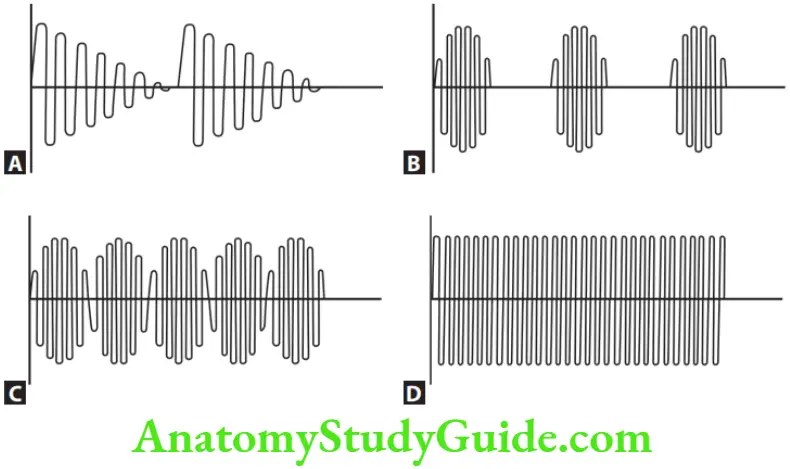
Four forms of electrosurgery current:
A. Unrectified, damped.
B. Partially rectified, damped (half-wave modulated).
C. Fully rectified (full-wave modulated).
D. Fully rectified, filtered (filtered).
Question 3. Name the various methods used in fluid control.
- Rubber dam
- High-volume vaccum
- Saliva ejector
- Svedopter
- Antisialagogues.
Question 4. What are the three factors which determine the suitability of gingiva for the use of rotary curettage?
- Absence of bleeding upon probing
- Sulcus depth less than 3.0 mm
- Presence of adequate keratinized gingival.
Question 5. What are the disadvantages of Svedopter?
- Difficult access to lingual surface
- Bruising the floor of mouth
- Interference – presence of mandibular tori
- Provoke gag reflex.
Question 6. What are the different methods of finish line exposure?
- Mechanical
- Chemicomechanical and surgical
- Rotary curettage and electrosurgery.
Question 7. State the three criterias for a gingival retraction material.
- Effectiveness in gingival displacement and hemostasis
- Absence of irreversible damage to the gingiva
- Paucity of untoward systemic effects.
Question 8. Name the electrodes.

A. Coagulating.
B. Diamond loop.
C. Round loop.
D. Small straight.
E. Small loop.
Fill in the blanks
Question 1. _______________ the most effective of all isolation devices utilized in dentistry.
Answer. Rubber dam
Question 2. Rubber dam should not be used with _______________ impression material.
Answer. polyvinyl siloxane
Question 3. Cord impregnated with _______________ is the most commonly used means of producing gingival retraction in chemicomechanical method.
Answer. 8% racemic epinephrine
Question 4. Electrosurgery is contraindicated in patients with _______________.
Answer. Cardiac pacemakers
Leave a Reply