Antiprotozoal Agents Introduction
Amoebiasis is a protozoal disease caused by protozoan Entamoeba histolytica. Amoebic infections generally remain confined to the intestine, where they may give rise to dysentery, but in an appreciable fraction of cases, the amoebae may be located elsewhere, especially in the liver. The chemotherapy of amoebiasis thus must provide drugs to treat both the intestinal and extraintestinal forms of the disease.
Table of Contents
Antiprotozoal Agents Classification
- Drugs used in intestinal amoebiasis:
- Examples: Diloxanide furoate, Iodoquinol, Pentamidine isethionate, Atovaquone, Ornithine, Dimercaprol.
- Drugs used in extraintestinal amoebiasis:
- Examples: Emetine, Dehydroemetine, Chloroquine.
- Drugs used for both intestinal and extraintestinal amoebiasis:
- Examples: Metronidazole, Tinidazole, Furazolidone, Nitazoxanide, Ornidazole, Secnidazole, Satranidazole
Intestinal Amoebiasis
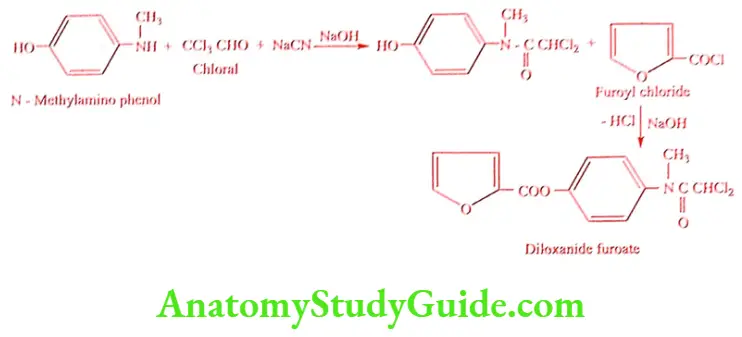
Diloxanide furoate (Dyrade-M, Dialox)
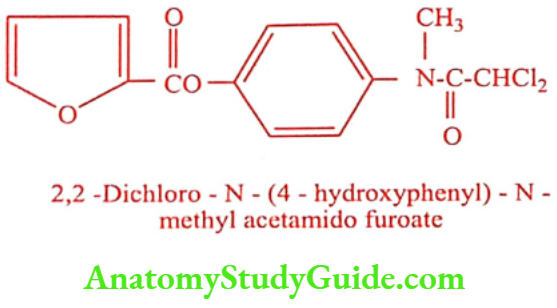
Synthesis
ADR: Head ache, dizziness, seizures and metallic taste.
Dose: 500mg three times a day for 5 to 10 days.
Use: It is the drug of choice for the treatment of symptomatic passers of cysts. It is ineffective when administered alone in the treatment of extra intestinal amoebiasis. It has been combined with Imidazole and Metronidazole.
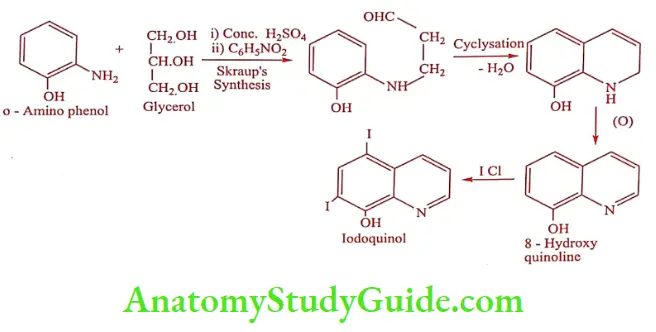
Iodoquinol (Diodoquin, Doquinol)
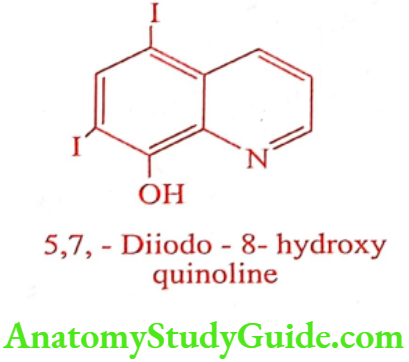
Synthesis
ADR: Neuropathy and visual impairment.
Dose: 650mg three times daily for 20 days.
Use: It is the drug of choice for the treatment of symptomatic infections caused by Entamoeba histolytica. In symptomatic intestinal disease, it is combined with Metronidazole to treat mild to moderate infections. It is ineffective in the treatment of extraintestinal amoebiasis such as a hepatic abscess.
Extra Intestinal Amoebiasis
Emetine
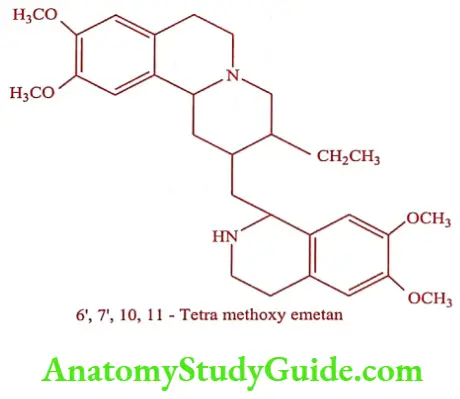
The alkaloid emetine and dehydroemetine are obtained from the extracts of ipecac (Cephaelis ipecacuanha). They occur a levorotatory form.
ADR: Dizziness, diarrhea, headache, and vomiting.
Dose: 1 to 1.5mg/kg/day up to 90mg for 5 days.
Use: It exhibits a direct amoebicidal action on various forms of E.histolytic. It is also used to treat balantidial dysentery and fluke infestations such as fascioliasis and paragonimiasis.
Chloroquine
It kills trophozoites of E.histolytic, and it is highly concentrated in the liver. Therefore, it is used in hepatic amoebiasis only.
Both Intestinal and Intestinal Amoebiasis
Metronidazole (Flagyl, Metrogyl)
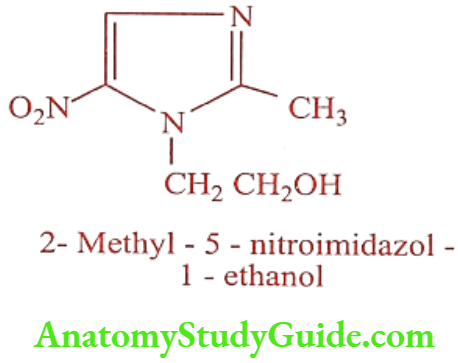
Synthesis
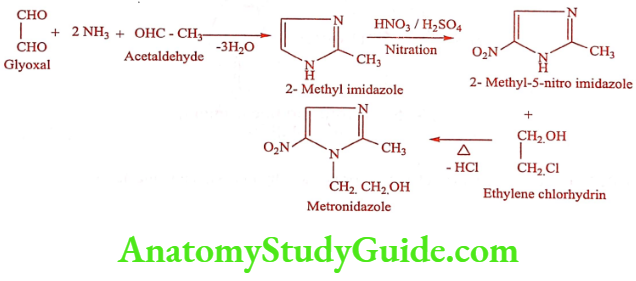
ADR: GI disturbances, metallic taste, and diarrhea.
Dose: 400 to 800mg three times daily for 5 to 10 days.
Use: It is an effective amoebicide and drug of choice for the treatment of all symptomatic forms of amoebiasis.
Tinidazole (Tina, Tiniba)
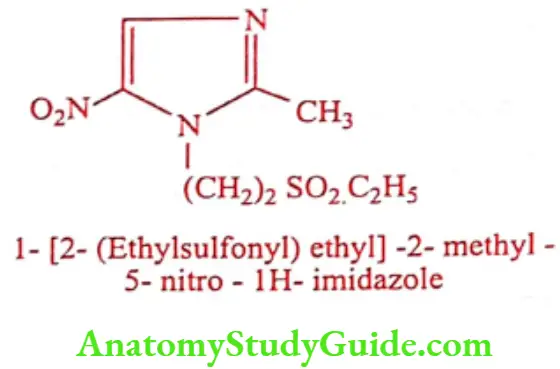
Synthesis
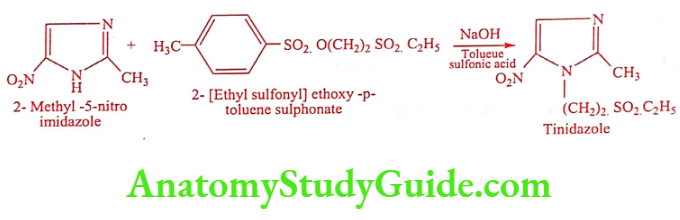
ADR: Metallic tasty, nausea and headache.
Dose: 2gm/day for 3 days, taken along with food.
Use: It is used in the treatment of intestinal and hepatic amoebiasis.
Furazolidone (Furoxone, Lomofen)
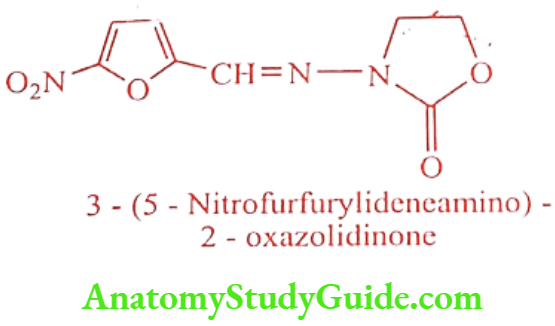
ADR: Hypersensitivity, hypoglycemia, orthostatic hypotension, and dizziness.
Dose: 100mg, 4 times daily.
Use: It is used in the treatment of diarrhea and enteritis caused by bacteria or protozoan infections.
Nitazoxanide (Nita cure, Nitazet, Nozoa)
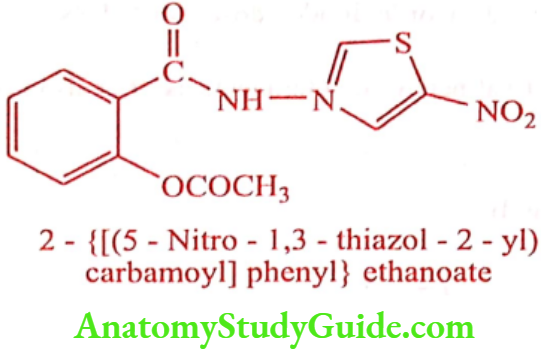
ADR: Headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
Dose: 7.5mg/kg twice daily.
Use: It is used in the treatment of diarrhea caused by Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia lamblia, and also used in the treatment of illness caused by other protozoa and/or helminths infections.
Ornidazole (Dazolic, Ornizen)
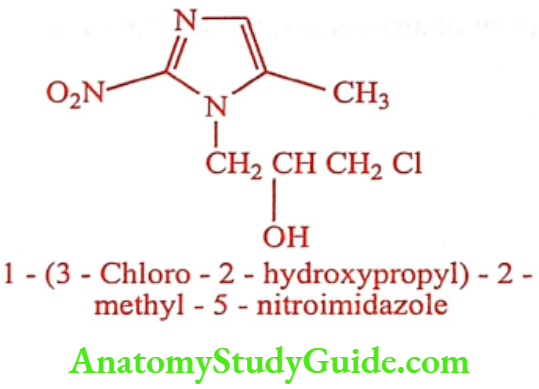
ADR: Somnolence, headache, nausea, dizziness and tremor.
Dose: 1.5gm as a single dose for 3 days.
Use: It is used in the treatment of Crohn’s disease.
Secnidazole (Entosec, Etisec, Seczol)
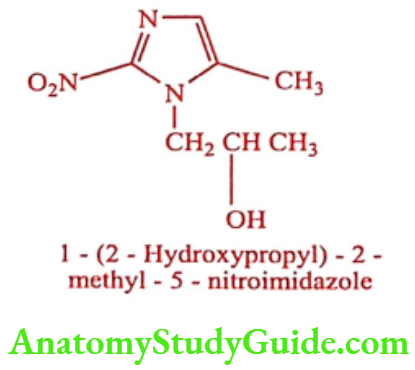
ADR: Nausea, gastralgia, changes of taste and metallic taste.
Dose: 1.5gm daily as a single dose or in divided doses for 5 days.
Use: It is effective in the treatment of dientamoebiasis. It is also active against Atopobium vaginae
Satranidazole (Satrogyl)
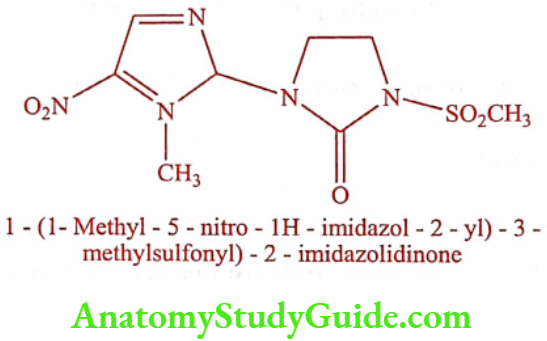
ADR: Headache, dry mouth, weakness, and dizziness.
Dose: 300mg bid for 10 days.
Use: It is used in the treatment of amoebiasis, trichomoniasis, and giardiasis.
Leave a Reply