Urinary Tract Anti-Infective Agents Introduction
A number of organic compounds obtained by chemical synthesis on the basis of model compounds have useful antibacterial activity for the treatment of local, systemic and urinary tract infections. Quinolone antibacterial drugs have been in use since 1964 when Nalidixic acid was discovered. They are highly active against most of the Gram- negative pathogens including Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacteria. Newest fluoroquinolone like Levofloxacin are active against Streptococcus pneumonia. Fluoroquinolones are used to treat upper and lower respiratory infections, gonorrhea, bacterial gastroenteritis, skin and soft tissue infections.
Table of Contents
Urinary Tract Anti-Infective Agents Classification
Chemical classification of synthetic antibacterial agents includes.
- Sulfonamides :
- Examples: Sulfadiazine, Sulfacetamide, Trimethoprim.
- Quinolones:
- First-generation quinolones :
- Example: Nalidixic acid, Cinoxacin.
- Second-generation quinolones:
- Example:Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Gatifloxacin, Sparfloxacin, Balofloxacin, Enoxacin.
- First-generation quinolones :
- Nitro furans :
- Example: Nitrofurazone, Furazolidone, Nitrofurantoin.
- Methenamine and its salts :
- Example: Methenamine, Methenamine mandelate, Methenamine hippurate.
Sulfonamides
Quinolones
The quinolone antibacterial comprises a group of synthetic substances possessing a common N-1-alkylated-3-carboxy-4-one ring fused to another aromatic ring.
Structure Activity Relationship
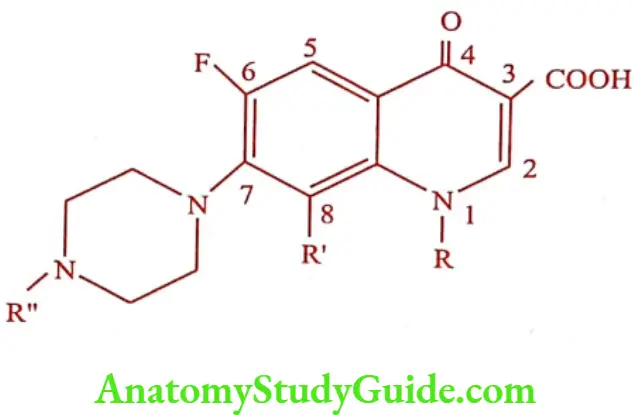
- The general structural requirements for antibacterial activity can be summarized as1,4-Dihydro-4-oxo-pyridin-3-carboxylic acid moiety is essential for antibacterial activity.
- The pyridone system must be annulated with an aromatic ring.
- Replacement of nitrogen for carbon at position 2, 5, 6 and 8 are consistent with retention of antibacterial activity.
- Introduction of substituents at position 2 greatly reduces the activity.
- Presence of 4-oxo group is must for activity.
- Fluorine atom substitution at position 6 is associated with significantly enhanced antibacterial activity.
- Alkyl substitution at position 1 is essential for activity. Lower alkyl group (methyl, ethyl, cyclopropyl) compounds are having greater potency.
- Aryl substitution at position 1 is also having consistent activity.
- Amino substitution at position 5 gives active compound.
- Piperazine, N-methyl piperazine and pyrrolidine ring substitution at position 7 gives active compounds.
- Chlorine substitution at position 6 results in an active compound.
First Generation Quinolones
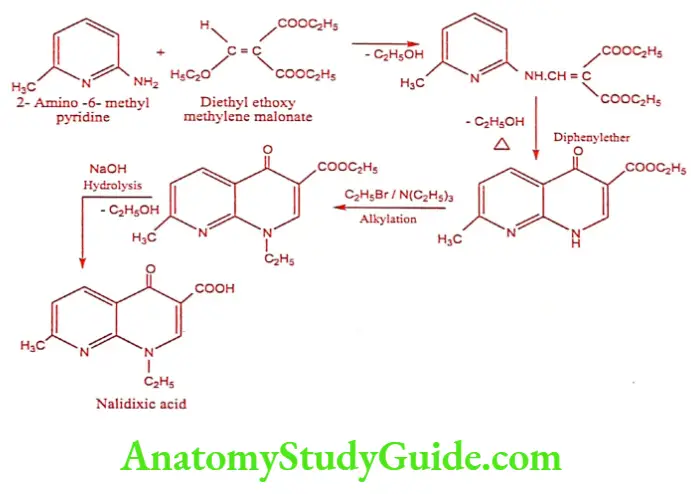
Nalidixic acid (Gramoneg, Negadix)
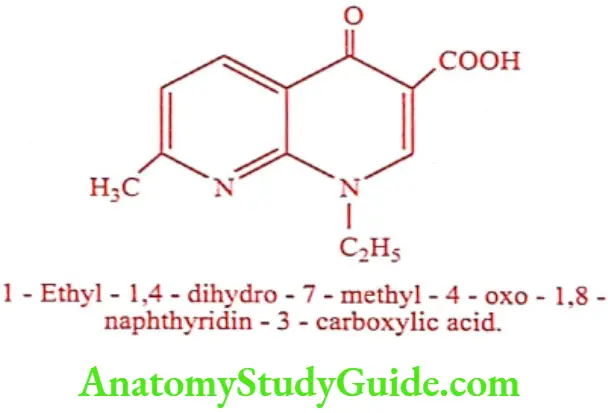
Synthesis
ADR: Photosensitive reactions, pruritis and nausea.
Dose: 1gm 4 times daily for 1 to 2 weeks.
Use: It is particularly effective against Gram-negative a bacterium that causes urinary tract infection.
Second Generation Quinolones
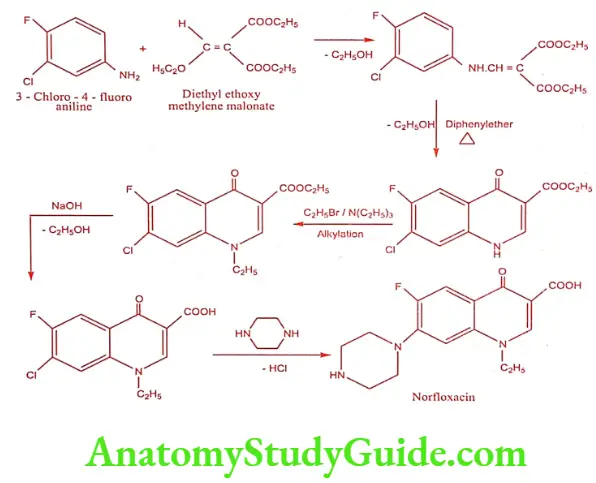
Norfloxacin (Norbactin, Norflox)
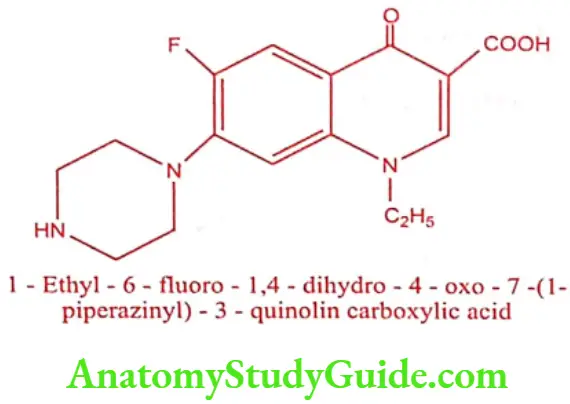
Synthesis
ADR: Nausea, vomiting and metallic taste.
Dose: 400mg/kg twice daily.
Use: It is indicated for the treatment of urinary tract infections caused by E.coli, K.pneumoniae and P.mirabilis, indole-positive Proteus spp. including P.vulgaris, P. aeruginosa, S.aureus and S.epidermidis and group – D Streptococci.
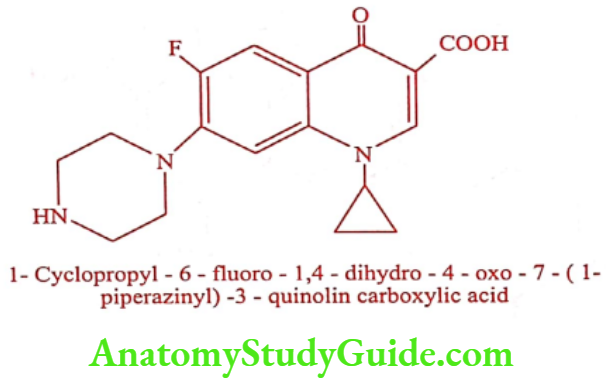
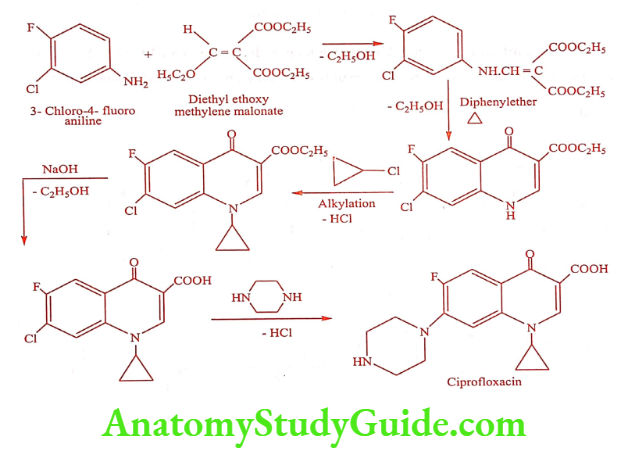
Ciprofloxacin (Cifran, Ciplox, Cipride)
Synthesis
ADR: GI disturbance, headache and tremor.
Dose: 250 to 750mg bid.
Use: It is a very effective drug for the treatment of urinary tract infection.
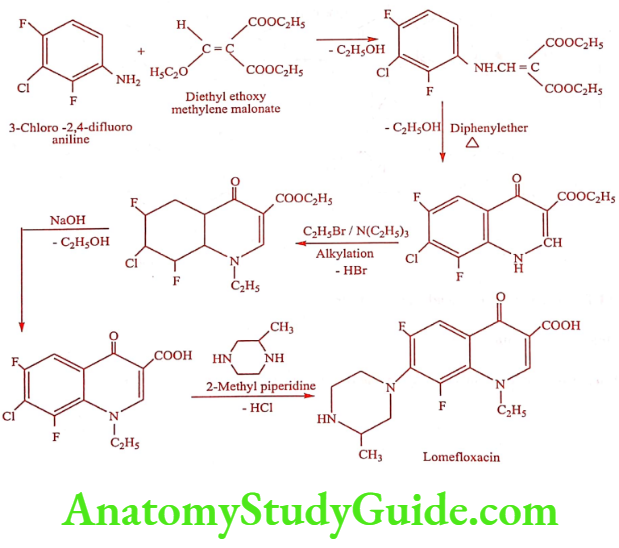
Lomefloxacin (Lomef-400, Lomedon, Okacyn, Uniquin)
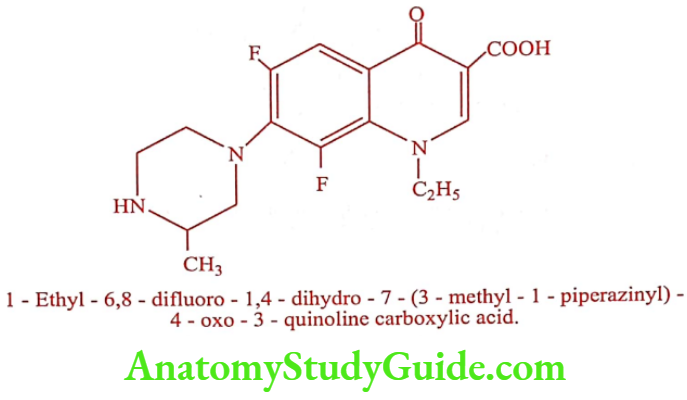
It is a difluorinated quinolone with a longer elimination half-life (7 to 8 hours) than any other member of this class. It is the only quinolone once daily oral dosing suffices.
Synthesis
ADR: It is associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. Nausea, abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Dose: 400mg once daily.
Use: It is used in the treatment of acute cystitis, bacterial infections including bronchitis and chronic urinary tract infections. It is also used to prevent urinary tract infections prior to surgery.
Ofloxacin (Chekmet, Oflox, Zanocin)
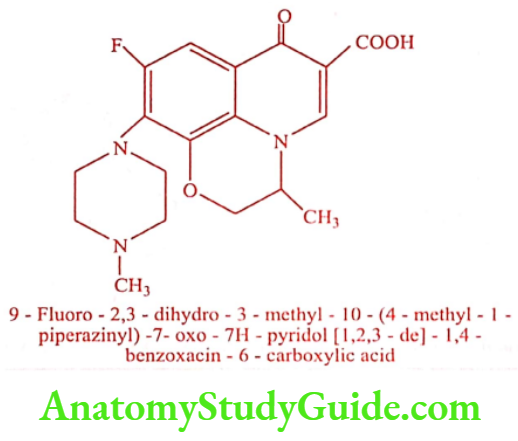
It is a synthetic chemotherapeutic antibiotic of second generation fluoroquinolone derivative. It is a racemic mixture consists of 50% levofloxacin (biologically active form) and 50% dextrofloxacin. It stops the multiplication of bacteria by inhibiting the reproduction and repair of their genetic material (DNA).
ADR: Tendon damage, peripheral neuropathy, hepatotoxic, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, insomnia, head ache, dizziness, itching and vaginitis in women.
Dose: 200mg bid.
Use: It is used in the treatment of infections of lower respiratory tract, including chronic bronchitis and pneumonia caused by Gram-negative bacilli and pelvic inflammatory disease and is highly active against both Gonococci and Chlamydia.
Sparfloxacin (Sparmax, Sparflo)
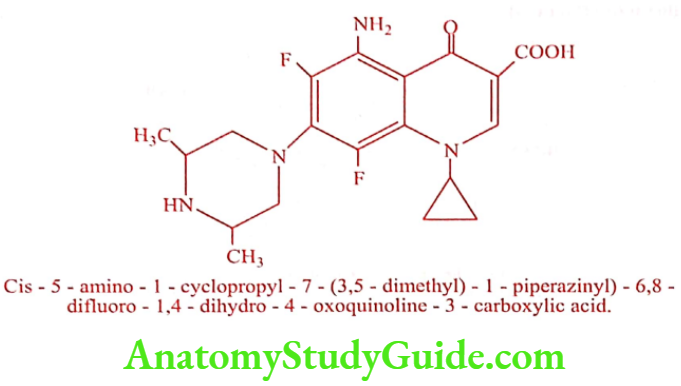
Synthesis
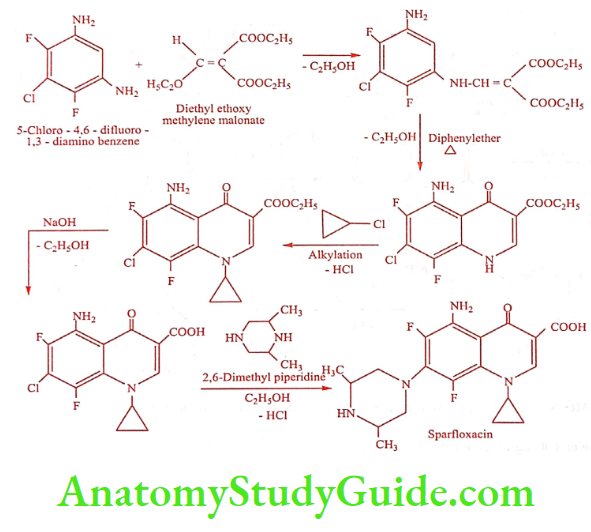
ADR: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
Dose: 100 to 300mg daily as a single dose or two divided doses.
Use: It is a newer fluoroquinolone, effective against Staphylococci, Streptococci and Chlamydia.
Balofloxacin (Bazucin)
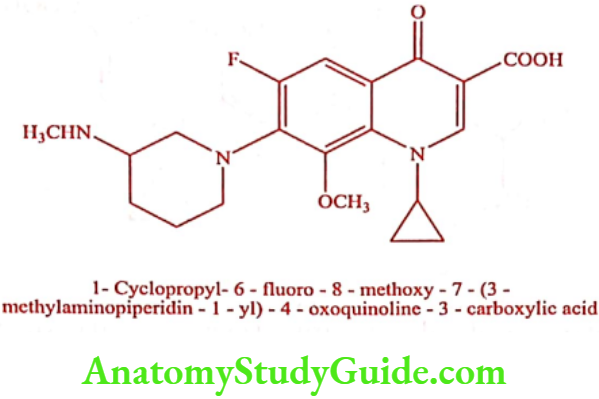
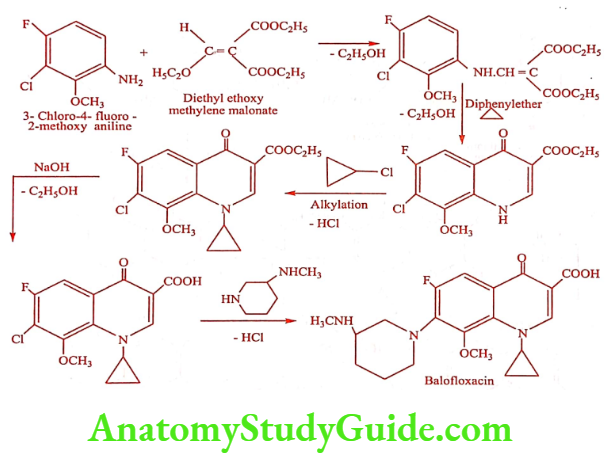
Synthesis
ADR: Nausea, heart burn, dizziness, fever, indigestion and urticaria.
Dose: 100mg twice daily.
Use: It is used to treat various types of infections including severe urinary tract infection.
Nitrofurans
Nitro furans are the first heterocyclic compound introduced in chemotherapy. They are used for the treatment of various kinds of bacterial infections. Nifurimox is used as an antiprotozoal agent to treat trypanosomiasis and leishmaniasis. Another important nitro heterocyclic is Metronidazole, which is used in the treatment of systemic infections caused by anaerobic bacteria.
The nitro furans are derivatives of 5-Nitro-2-furaldehyde. Antimicrobial activity is present only when the nitro group is in 5th position.
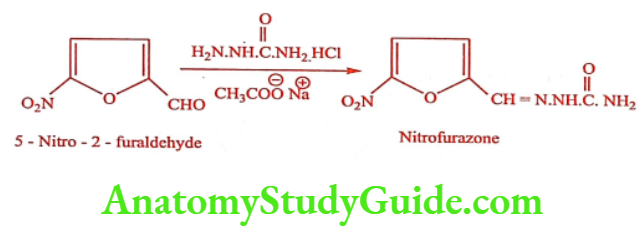
Nitrofurazone (Furacin)
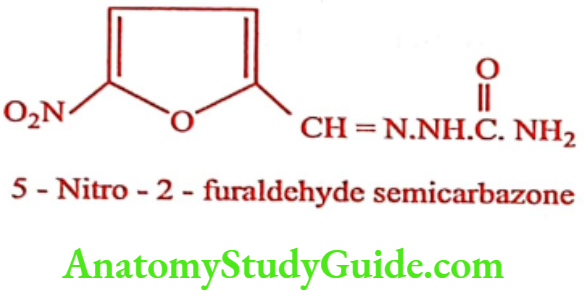
Synthesis
ADR: Severe peripheral neuropathy.
Dose: 0.2% topical preparation in a water soluble basis to the affected area.
Use: It is used topically in the treatment of burns. It has a broad spectrum activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, but it is not active against fungi.
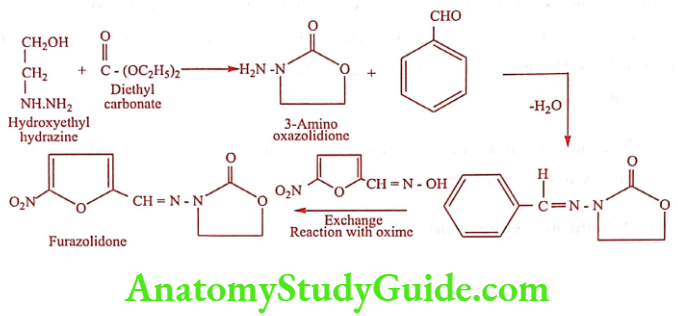
Furazolidone (Furoxone, Lomofen)
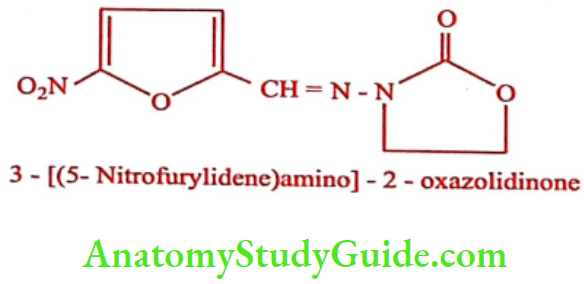
Synthesis
ADR: Hypersensitivity, hypoglycemia and dizziness.
Dose: 100mg, 4 times daily.
Use: It has bactericidal activity against S.aureus, E.coli, Salmonella, Shigella, Proteus spp, Enterobacter and Vibrio cholerae. It is recommended for the oral treatment of bacterial or protozoal diarrhea caused by susceptible organisms.
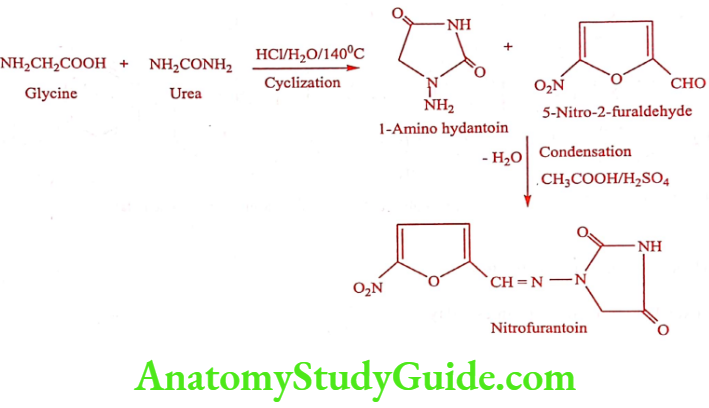
Nitrofurantoin (Furadantin)
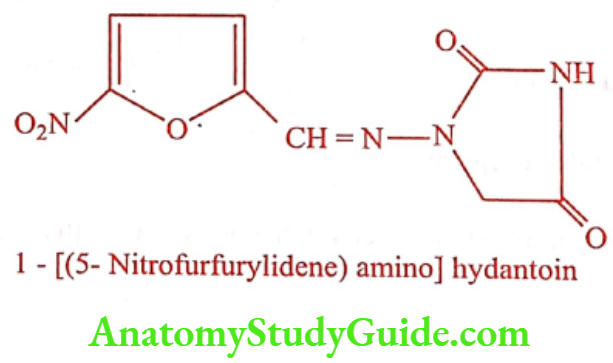
Synthesis
ADR: Anorexia and diarrhea.
Dose: 50 to 100mg, 4 times daily for 7 days.
Use: It is effective against a majority of urinary tract pathogens, including certain strains of E.coli, Klebsiella, Proteus sp, Pseudomonas and Aerobacter sp. It is also effective against many Staphylococci, Clostridia and Bacillus subtilis.
Methenamine and its Salts
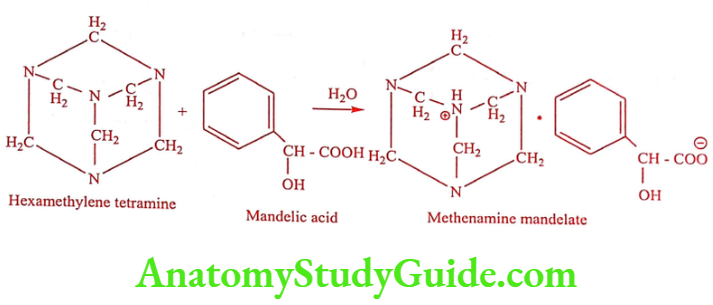
Methenamine mandelate (Mandelamine)
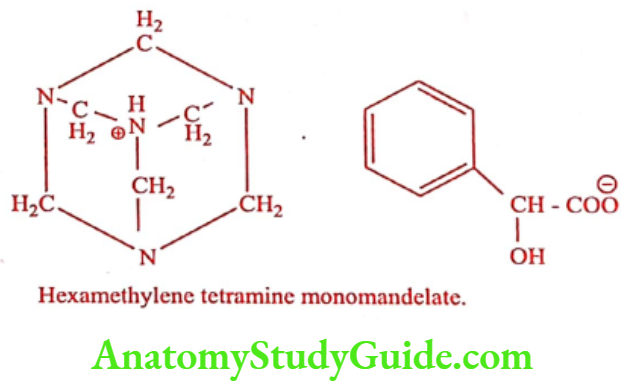
Synthesis
ADR: Gastritis and haematuria.
Dose: 1gm three or four times a day.
Use: It is used as urinary tract anti-infective agent.
Leave a Reply