Implant Prosthesis Definition
Dental implant is defined as “a prosthetic device made of alloplastic material implanted into oral tissues beneath the mucosal or/and periosteal layer, and on/or within the bone to provide retention and support for a fixed or removable dental prosthesis”. A substance that is placed into or/and upon the jaw bone to support a fixed or removable dental prosthesis.
Table of Contents
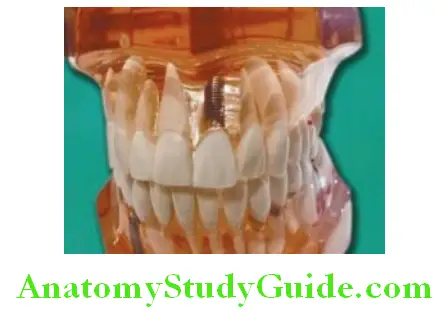
Dental implants are basically root form of some metallic alloy mainly containing medical grade pure titanium. These implants are inserted into alveolar bone or jaw bone to fix with bone tissue by process known as osseointegration. See photographs of transparent model here to understand the process of implant placement in the bone.
Read and Learn More: Preclinical Prosthodontics Notes
Implant Prosthesis Indications
Dental implant can be used to support any kind of dental prosthesis. Implants can be used for retention and support of extraoral prosthesis.
Implants are indicated for:
- Partial edentulous conditions
- Complete edentulism
- Implant supported fixed dental prosthesis
- Rehabilitation of maxillofacial defects with implant supported prosthesis.
Implant Prosthetic Components
The implantation of prosthetic components is described.
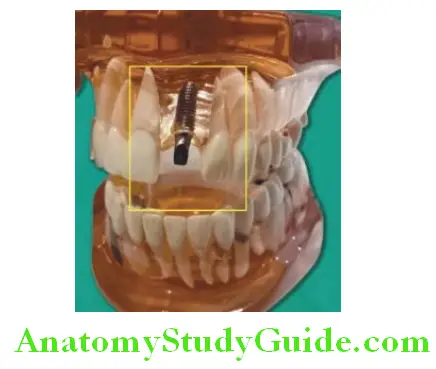
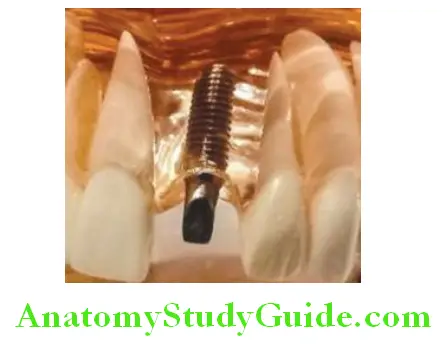
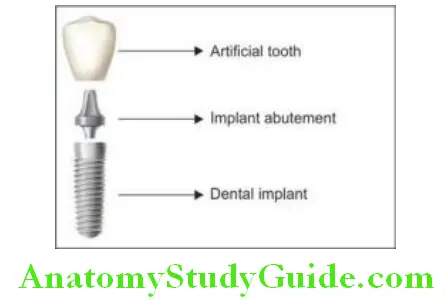
Single Tooth Replacement
To replace single missing tooth implant is widely used. A single root form implant is placed in place of missing tooth. Once the osseointegration is done, an implant abutment is fixed on the implant with screw. The artificial tooth (crown) is then cemented or fixed on abutment with screw.
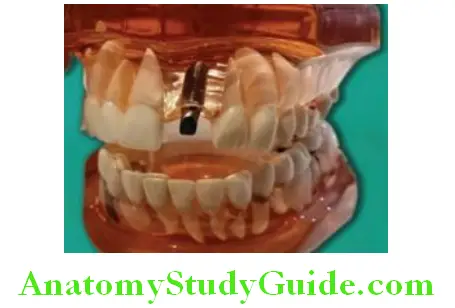
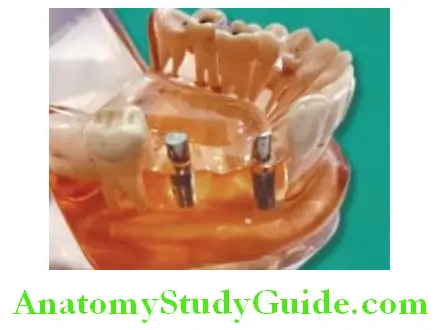
Replacement Of Multiple Missing Teeth
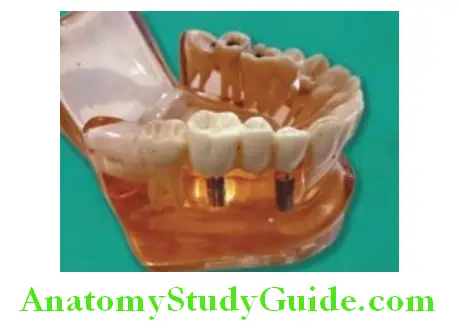
Dental implants can be used for replacement of more than one missing teeth. Prosthesis (bridge) can be fixed on implants to replace multiple missing teeth. Model showing two implants placed to replace three missing teeth. Three unit prosthesis is fixed on implant abutments to replace three missing.
Leave a Reply